Human-Centered Design
What is Microsoft's approach to digital accessibility and why is it important?
Microsoft views access to technology as a fundamental human right, recognizing that over a billion people worldwide live with some form of disability. The company has evolved its accessibility strategy by integrating both technical innovations and inclusive organizational practices. Despite rapid digital transformation across industries, the disability divide is growing, with only 4% of businesses considering accessibility in their strategy. This represents a significant business opportunity, as organizations with inclusive technology strategies demonstrate better revenue and profit margins. Microsoft's journey includes establishing employee resource groups, hosting regular ability summits, and creating the Inclusive Tech Lab to ensure products are accessible to everyone, regardless of whether their disabilities are permanent, temporary, or situational.
Watch clip answer (06:25m)What is universal design in the context of map accessibility?
Universal design in map accessibility is an aspirational approach originating from architecture that focuses on making maps usable by all people to the greatest extent possible. Rather than just addressing blindness, it considers a broader range of impairments including common vision problems and cognitive challenges. Amanda Tickner emphasizes this paradigm as a goal rather than a specific set of guidelines, recognizing limitations while striving for improvement. This approach prioritizes enhancing comprehensibility for everyone instead of merely accommodating regulations, making it a more effective framework than focusing on specific disabilities alone.
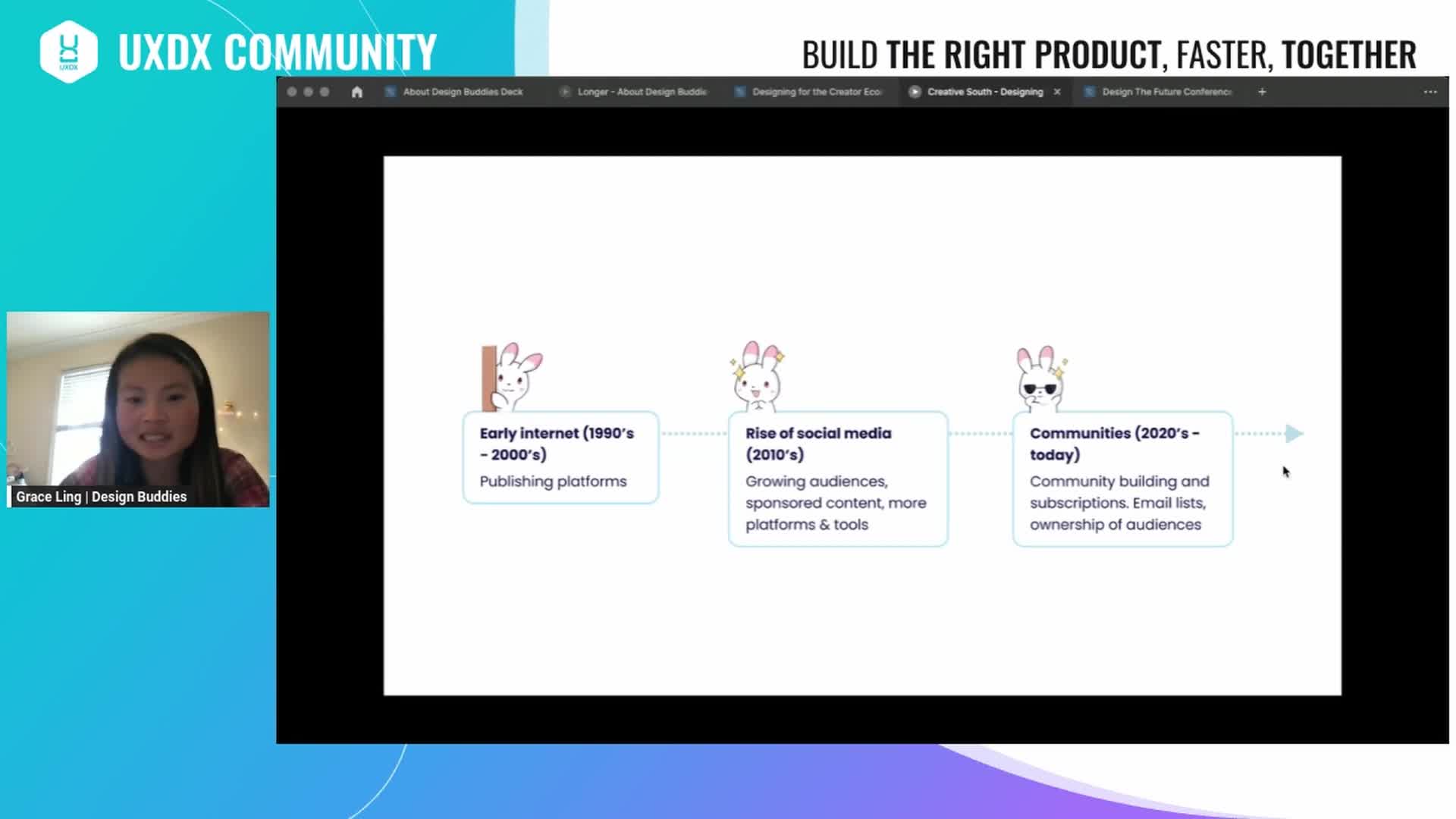
Watch clip answer (01:44m)How should designers effectively use AI in their workflow?
Designers should use AI as a starting point and then add their own personality and ideas to maintain individuality. Grace Ling recommends being mindful when building or using AI tools, as they significantly increase production speed. While AI won't replace designers entirely, Grace believes it will replace those who don't adopt it. She emphasizes that AI can create new forms of content through human-AI collaboration, making it important for designers to learn how AI fits into their workflow to enhance creativity and productivity rather than seeing it as a replacement.
Watch clip answer (00:16m)How does empathy influence design thinking?
Empathy influences design thinking by allowing designers to observe the world through others' perspectives, putting aside preconceptions to understand users' needs at an emotional and psychological level. It fuels creativity that transforms into human-centered solutions by creating a bond between developers and users. David Kelley, IDEO's founder, explains design thinking as deeply understanding problems and realities of people you're designing for, meeting their needs in technologically feasible and strategically viable ways. Airbnb's success story demonstrates how empathy-driven design—improving listing photos—doubled their revenue and transformed their business.
Watch clip answer (03:45m)What is the reflective level of processing in design according to Don Norman?
According to Don Norman, the reflective level is the third level of processing in design, comparable to the superego. It functions as an observing part of the brain that doesn't directly control sensory input or muscle movement, but instead monitors our experiences and reactions. This reflective component acts as an internal voice that provides commentary on our interactions, saying things like 'that's good' or 'that's better' and questioning our actions. While it lacks direct control over our behaviors, it serves as a critical evaluative mechanism that helps us process and make meaning of our experiences with design.
Watch clip answer (00:24m)How does happiness affect problem-solving and creative thinking?
According to Don Norman, when people are happy, their brains process information differently, making them more creative problem solvers. Psychologist Alice Ison demonstrated this in an experiment where students who received candy (making them slightly happier) were able to solve a challenging string-tying problem, while anxious students could not. Happiness triggers dopamine release in the prefrontal lobes, promoting breadth-first processing and out-of-the-box thinking. This enables more creative solutions and lateral thinking - the principle behind brainstorming sessions. Meanwhile, anxiety and fear cause depth-first processing, which helps with focus and meeting deadlines but limits creative thinking. This explains why pleasant experiences in design not only feel better but actually function better.
Watch clip answer (00:02m)