Financial Analytics
What are the different types of revenue streams and why are they important for businesses?
Revenue streams represent the various ways businesses generate income, categorized as operating revenues (from core business activities like Coca-Cola selling drinks) and non-operating revenues (from side activities like interest, rent, and dividends). These streams follow different models: transaction-based (one-time payments), service (time-based billing), project (large one-time tasks), and recurring revenue (subscription or licensing fees). Understanding these revenue streams is crucial for financial analysts as they significantly impact business evaluation and forecasting. Each type has unique implications for cash flow predictability—recurring revenues provide consistent income, while transaction-based and project revenues fluctuate with demand. This knowledge helps analysts accurately evaluate business sustainability and develop appropriate forecasting models for different revenue types.
Watch clip answer (04:18m)What is ROI and how is it calculated in project management?
Return on Investment (ROI) is a widely used measure of investment value in project management. It's calculated as the ratio of net income to total cost—specifically, (total income minus total cost) divided by total cost. This is typically expressed as a percentage by multiplying the fraction by 100. An ROI greater than 100% represents a positive return, indicating you get more out than you put in, while an ROI less than 100% represents a loss. Despite its popularity across business, public, and non-profit sectors, ROI has a key limitation: it doesn't account for the timing of costs and profits, which is especially important for long-term projects.
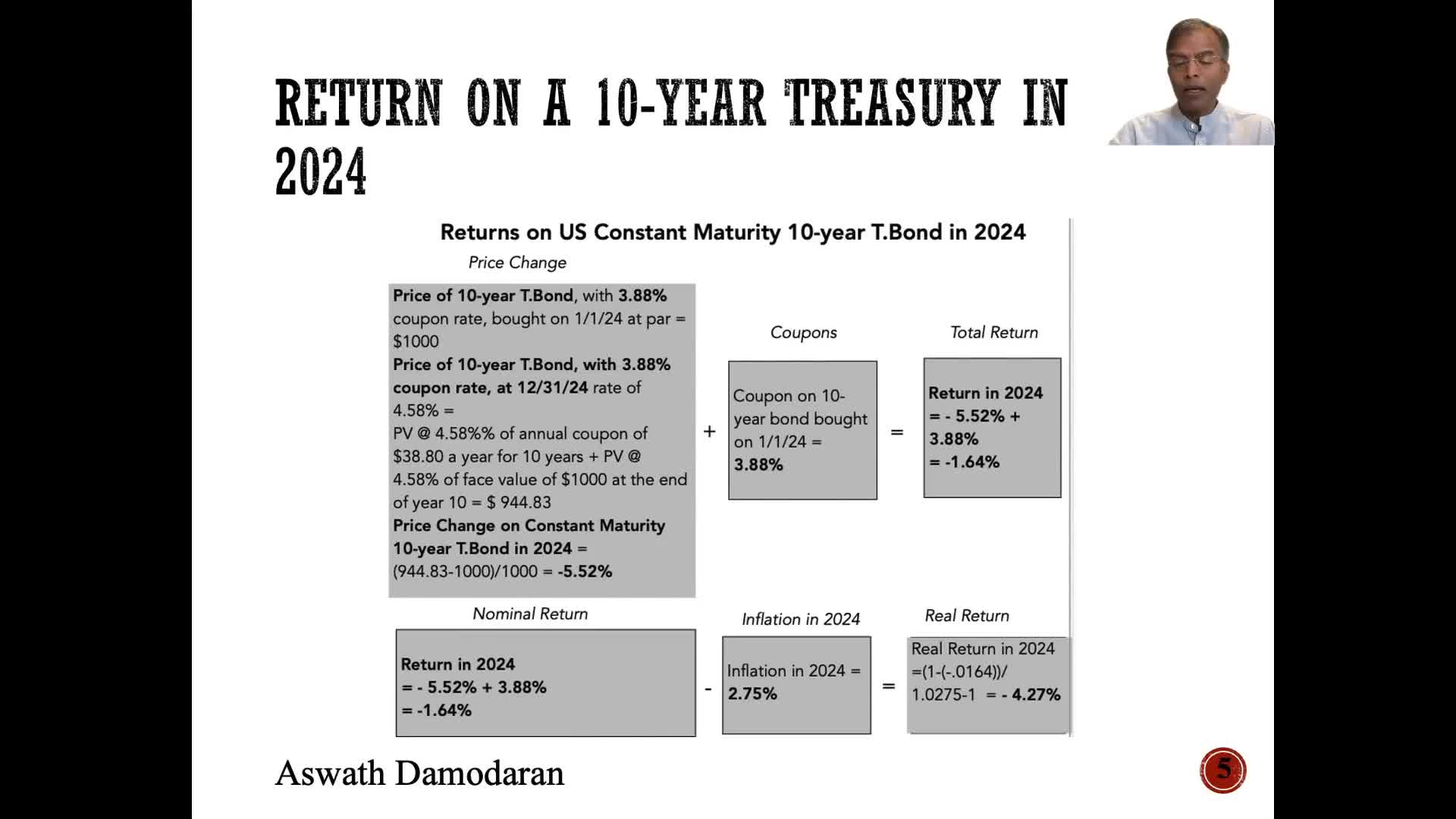
Watch clip answer (03:26m)What is the intrinsic risk-free rate and how does it explain interest rate movements?
The intrinsic risk-free rate provides a valuable framework for understanding why interest rates move over time. It represents the fundamental economic factors driving rates, distinct from the actual T-bond rate that fluctuated significantly in recent years. The difference between the intrinsic risk-free rate and actual T-bond rates was particularly notable when inflation spiked to 7-8% in 2022. Coming into 2025, this difference has narrowed to its lowest point in four years, reflecting changing economic fundamentals. These underlying economic factors, including inflation and real growth, are the primary drivers that determine interest rate movements across treasury and corporate bond markets.
Watch clip answer (00:24m)How can machine learning models improve credit scoring compared to traditional methods?
Machine learning models improve credit scoring by collating data across multiple sources including credit bureaus, bank accounts, money laundering statuses, and alternative payment histories. Unlike traditional credit scoring techniques, these ML models consider additional factors like monthly rental commitments that are typically overlooked. The model can explain which features are most important for credit decisions in layman's language, providing transparency. This approach creates a more sophisticated risk profiling system that delivers personalized credit recommendations, making the process more inclusive for applicants who might be underserved by conventional scoring methods.
Watch clip answer (01:39m)How did Asian markets perform on Wednesday?
Asian markets closed with mixed results on Wednesday as investors responded to recent earnings releases and economic indicators. Japan's Nikkei 225 showed gains, buoyed by strong corporate earnings, while Chinese markets struggled amid continued economic uncertainty. In India, the benchmark indices ended slightly lower after a volatile trading session. The Nifty index declined as heavyweight tech stocks faced downward pressure, though defense stocks continued to show strength in the broader market. This mixed performance reflects varying regional economic conditions and sector-specific trends across Asian markets.
Watch clip answer (00:27m)What is the current state of Indian stock markets and what are analysts predicting for near-term market movement?
The Indian stock markets experienced volatility with the Sensex falling by 29.47 points to close at 75,967.39 and the Nifty50 ending slightly lower. The indices tested a critical support level at 22,800 before staging a mid-session recovery. Sector performance was mixed with IT and energy sectors gaining while FMCG and auto sectors faced corrections. Analysts suggest markets may continue to trade sideways within the range of 22,800 to 23,100 in the near term. If Nifty breaks below 22,800, further correction may follow, while a move past 23,000 could signal renewed bullish momentum. Overall investor sentiment remains cautious as participants closely monitor global market trends and upcoming economic events.
Watch clip answer (01:16m)