Scientific Discoveries
What is the scientist's response to claims that federal layoffs are making America more efficient?
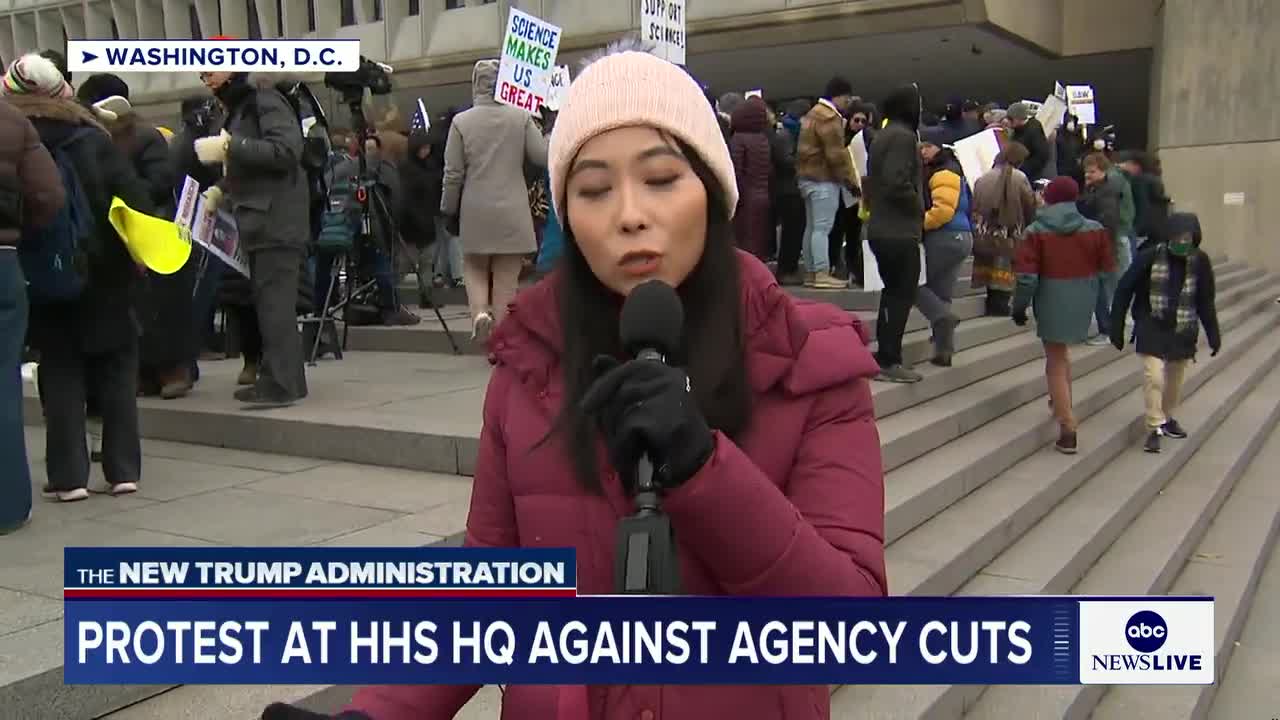
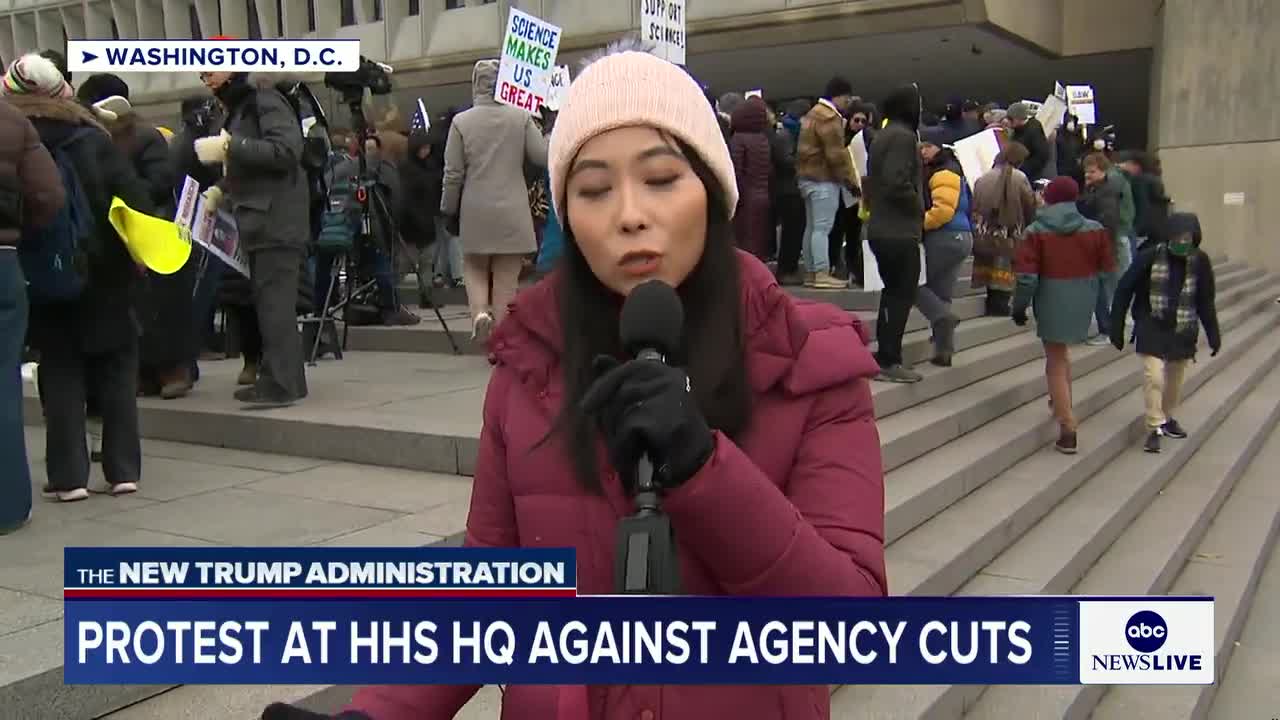
The NIH scientist firmly rejects the efficiency argument, stating it's not efficient to fire people indiscriminately based solely on HR forms without considering their actual work. She highlights how critical health and safety roles have been affected, including scientists working on nuclear weapons safety, bird flu, and substance use disorders. The scientist emphasizes that while the process may be efficient at firing people, it's not efficient at running government, as these indiscriminate cuts undermine important public health and safety initiatives.
Watch clip answer (01:06m)How are federal job cuts affecting health research in America?
Federal job cuts across the Department of Health and Human Services are severely impacting scientific research, with workers concerned about losing years of scientific progress. The layoffs are affecting scientists and researchers who have dedicated their lives to improving America's health, including those researching substance abuse and drug addiction prevention at the National Institutes of Health. One scientist who was recently laid off expressed fear about how these cuts will set back scientific research. The indiscriminate nature of the cuts, which include probationary workers, threatens to undermine critical health initiatives and vital ongoing research efforts that directly impact public health in America.
Watch clip answer (00:42m)How was the Saturn-like planet TVLM513B discovered?
TVLM513B was discovered by astronomers who detected it through a wobble in its star's motion, caused by the planet's gravitational pull. This marks the first time this detection technique was successfully employed using radio telescope observations, specifically the continent Wide Very Long Baseline Array. This method is typically used for detecting Jupiter-like planets in distant orbits from stars, making this discovery particularly significant. TVLM513B orbits a small, cool star approximately 35 light years away from Earth.
Watch clip answer (01:28m)How was the rare Saturn-like planet TVLM513B discovered?
TVLM513B was discovered by astronomers detecting a wobble in its star's motion caused by the gravitational pull of the planet. This marks the first successful application of this detection technique using a radio telescope, specifically the continent-Wide Very Long Baseline Array. The technique is typically used for detecting Jupiter-like planets in distant orbits from stars. Located about 35 light years from Earth, TVLM513B has a mass similar to Saturn and orbits in a path resembling Mercury's. This discovery is particularly significant because it's rare to detect extrasolar planets orbiting around small, cool stars.
Watch clip answer (01:16m)How was the Saturn-like exoplanet TVLM513B discovered?
The Saturn-like exoplanet TVLM513B was discovered using a gravitational wobble detection method. Scientists observed a distinctive wobble in the motion of a small, cool star located approximately 35 light years from Earth, which indicated the presence of this giant planet orbiting around it. This detection represents a significant advancement in observational astronomy, as the wobble technique has traditionally been used primarily for identifying Jupiter-like planets. By successfully applying this method to detect a Saturn-like planet around a smaller star, astronomers have expanded our capabilities for identifying various types of exoplanets in distant star systems.
Watch clip answer (00:08m)Is Atlantis a real historical civilization?
According to Johnny Harris, Atlantis has no basis in empirical fact. It was created by Plato as a parable to teach people, not as a historical account of a real civilization. While there are many who fill in knowledge gaps with their own interpretations that might make Atlantis seem real, this approach contradicts the scientific process. Scientific consensus, built through gathering, analyzing, and debating evidence over decades, does not support Atlantis's existence. Harris contrasts those who are comfortable making connections that feel good with the rigorous, slow process of establishing scientific knowledge through evidence-based consensus.
Watch clip answer (00:40m)