Scientific Breakthroughs
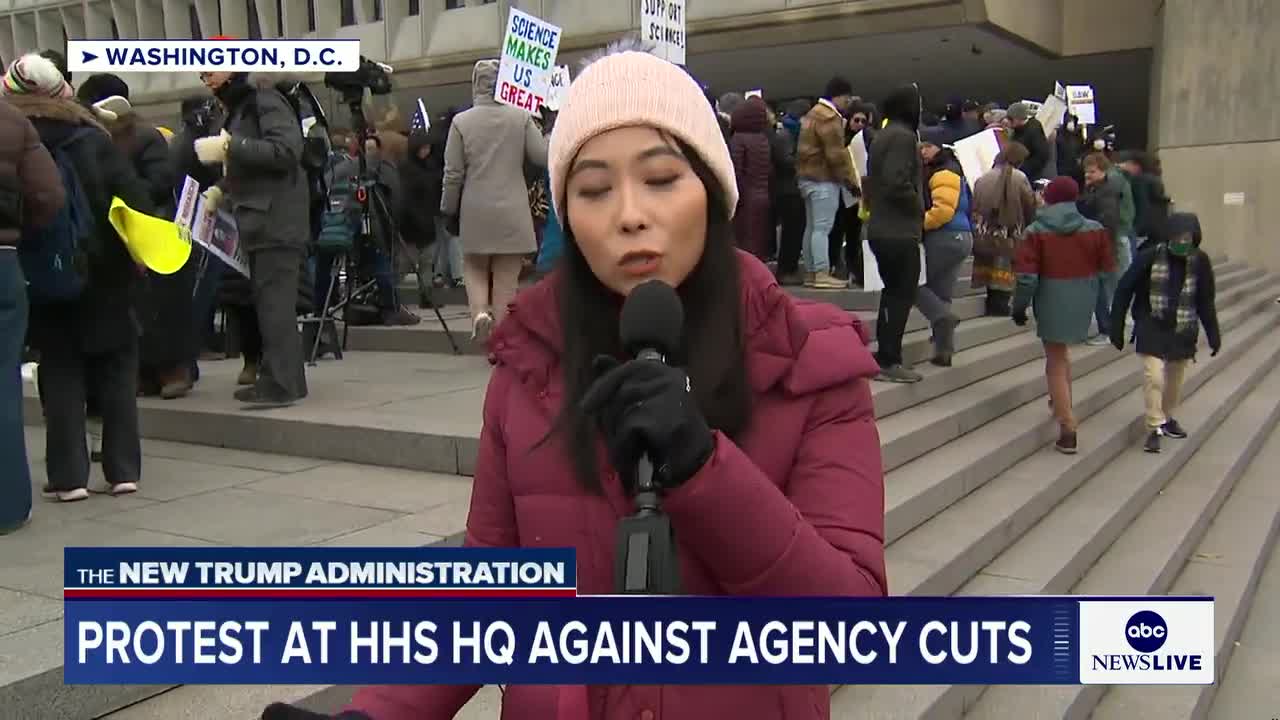
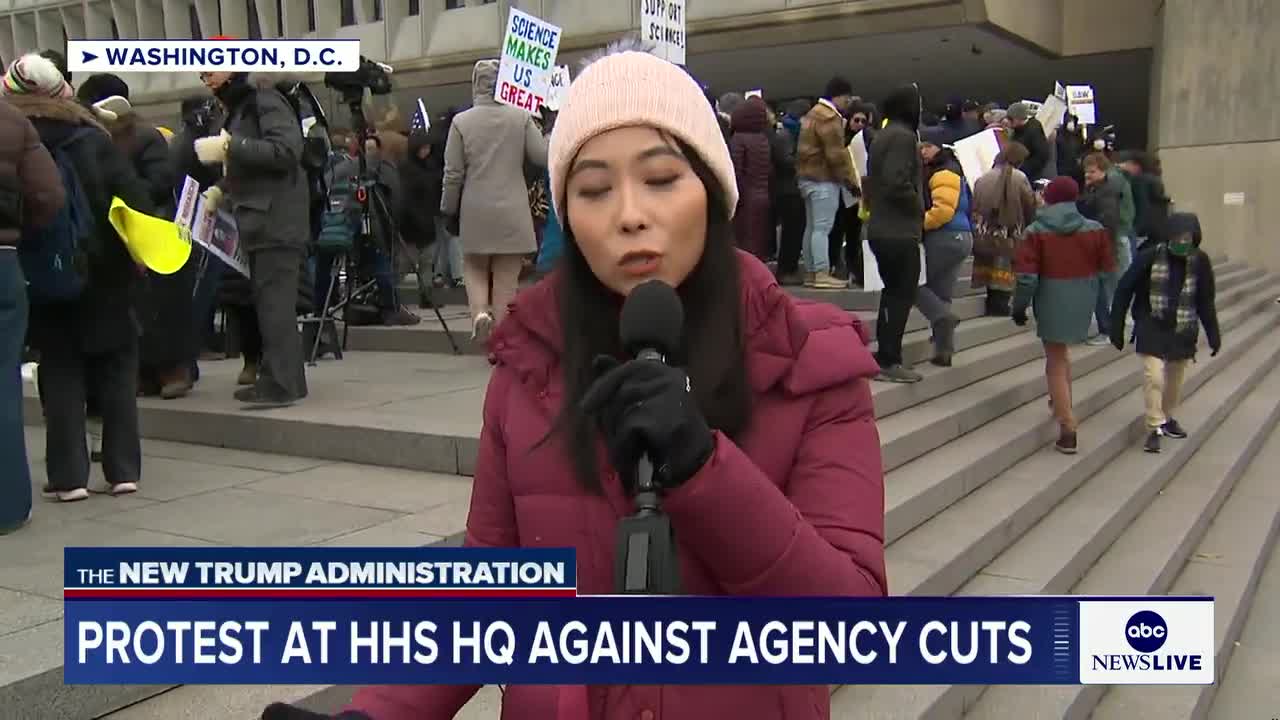
What are federal workers protesting at HHS headquarters in D.C.?
Federal workers are rallying against widespread cutbacks and firings at the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). The protesters, who have been demonstrating for over an hour with signs and chants, express significant anger and frustration over the situation. Their primary concern is that these cuts and layoffs will result in the loss of years of scientific progress. Many signs at the protest highlight how these workforce reductions threaten public health initiatives and scientific advancements developed over time.
Watch clip answer (00:33m)How are federal job cuts affecting health research in America?
Federal job cuts across the Department of Health and Human Services are severely impacting scientific research, with workers concerned about losing years of scientific progress. The layoffs are affecting scientists and researchers who have dedicated their lives to improving America's health, including those researching substance abuse and drug addiction prevention at the National Institutes of Health. One scientist who was recently laid off expressed fear about how these cuts will set back scientific research. The indiscriminate nature of the cuts, which include probationary workers, threatens to undermine critical health initiatives and vital ongoing research efforts that directly impact public health in America.
Watch clip answer (00:42m)How did the scientific revolution of the 1800s impact interest in the legend of Atlantis?
During the 1800s, Europe was undergoing a scientific revolution where empirical evidence was replacing religious explanations of reality. As European explorers discovered lost cities previously thought to be myths, curiosity about other legendary places intensified. These discoveries prompted scientists and explorers to wonder if Plato's Atlantis might also be real. While the idea of Atlantis existed earlier, it only gained serious traction during this period when science was 'having a big moment' and the possibility of finding advanced lost civilizations seemed more plausible through a scientific lens.
Watch clip answer (01:16m)What impact did the first image of a black hole have on public interest?
The release of the first-ever black hole image last year significantly amplified public interest in black holes and their anatomical structure. This groundbreaking visual evidence transformed what was previously a theoretical concept into something tangible that people could see, creating a surge of fascination about these cosmic phenomena. The image not only captured public imagination but also enhanced scientific understanding, serving as a catalyst for deeper exploration into how black holes might contain crucial information about our universe's history.
Watch clip answer (00:06m)What challenges did Hayabusa2 face during its landings on asteroid Ryugu, and what did it accomplish?
The Hayabusa2 mission encountered greater landing difficulties than anticipated due to Ryugu's extremely rocky surface. Despite these challenges, the spacecraft successfully completed two separate sample collection operations: the first gathering material from the asteroid's surface, and the second collecting underground samples, with each stored in separate compartments. Following initial examinations by JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), these valuable samples will undergo comprehensive analysis in Japan before being shared with NASA and other international research groups. This collaborative approach will maximize scientific insights from these rare extraterrestrial materials, potentially providing crucial information about the early solar system.
Watch clip answer (00:35m)What are JAXA scientists studying in the asteroid Ryugu samples and why is it important?
JAXA scientists are particularly focused on the organic materials found in the Ryugu asteroid samples. They're studying these materials to understand their distribution throughout the solar system and potential connections to life on Earth. This research could provide critical insights about the origins of our solar system and possibly reveal links to how life developed on our planet. The mission yielded more sample material than anticipated, which Seiichiro Watanabe, an Earth and environmental scientist from Nagoya University working with JAXA, considers excellent news. This abundance of material significantly expands their research capabilities, allowing for more comprehensive studies of these valuable extraterrestrial samples.
Watch clip answer (00:28m)