Human-Computer Interaction
How has the evolution of technology improved accessibility for visually impaired people?
The accessibility journey for visually impaired people has evolved significantly from Braille in the 1820s to talking books in the 1930s-40s, and audio cassettes in the 1960s. The most transformative development came in the late 1990s with e-books, which enabled visually impaired individuals to access content similarly to sighted readers through screen readers. Since 2000, the e-book revolution has dramatically improved electronic content accessibility, though challenges remain with scientific information, mathematical formulae, images lacking alt text, and legacy content that requires remediation to become accessible.
Watch clip answer (06:07m)What advancements has Neuralink achieved for quadriplegics and what are its future goals?
Neuralink has successfully implanted its technology in three quadriplegic patients, enabling them to control computers and phones directly with their thoughts through a product called 'telepathy.' This mind-controlled interface allows users to operate devices faster than people with working hands, restoring critical functionality for those with severe physical limitations. The next phase of Neuralink's development aims to place a second implant past the point of neural damage, potentially enabling paralyzed individuals to walk again. This ambitious goal focuses on restoring full body functionality by creating a neural bypass around damaged areas, which could revolutionize treatment options for people with spinal cord injuries.
Watch clip answer (00:41m)What progress has Neuralink made in helping quadriplegics and what are its future plans?
Neuralink has successfully implanted devices in three quadriplegic patients, enabling them to control phones and computers using only their thoughts - a capability they call 'telepathy.' These brain-computer interfaces allow users to operate technology faster than people with functioning hands by directly translating neural signals into digital commands. The next phase of Neuralink's development involves adding a second implant beyond the point of neural damage to restore mobility. This additional implant would potentially enable patients with spinal cord injuries to regain full body functionality, including the ability to walk again, addressing a core limitation of quadriplegia.
Watch clip answer (00:46m)What are the main usability issues with Windows 11's Settings menu that frustrate users?
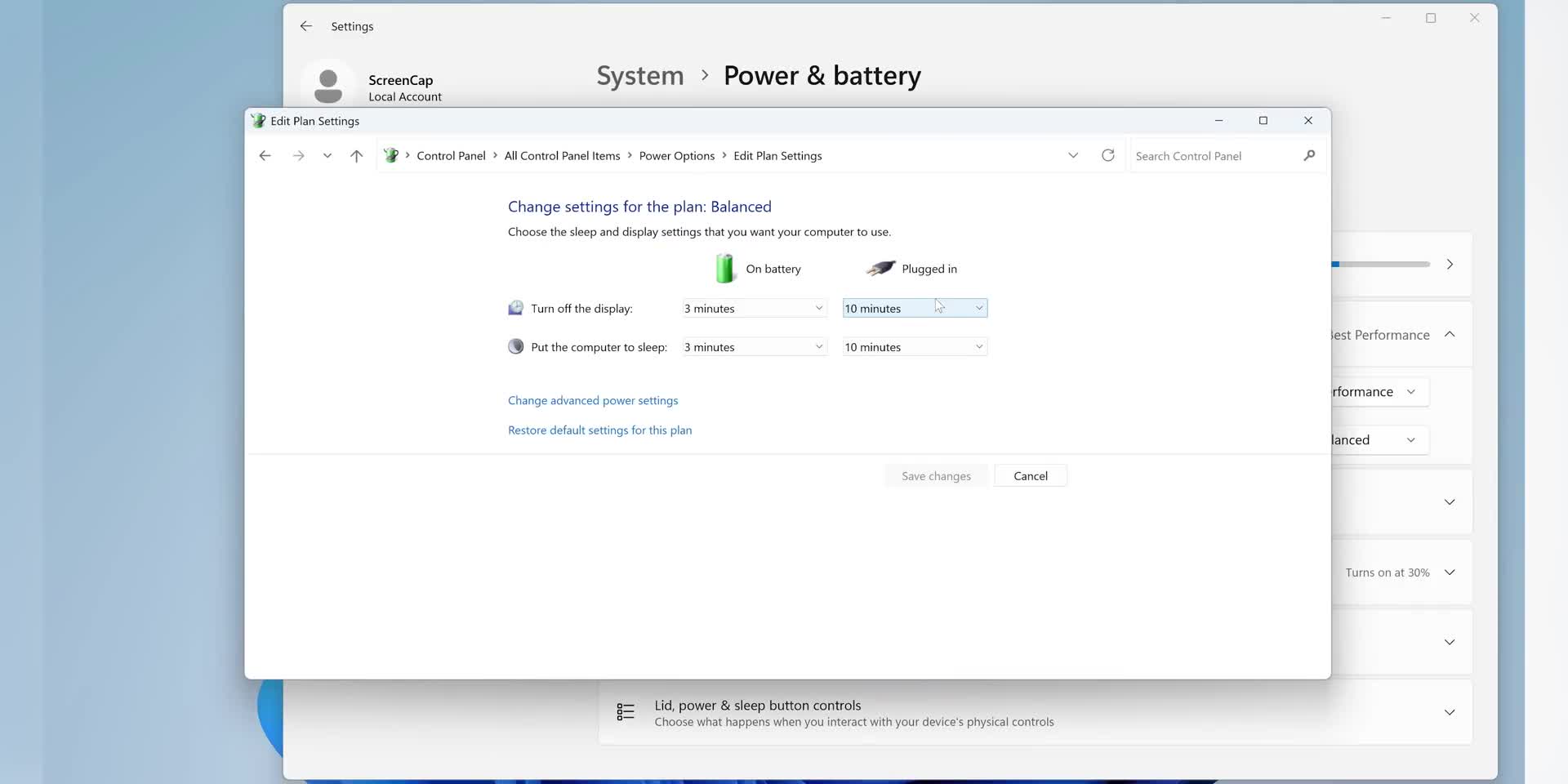
Windows 11's Settings menu suffers from significant usability problems that create daily frustrations for users. The most prominent issue is the restriction to only one settings window at a time, forcing users to constantly navigate back and forth between different sections when they need to adjust multiple settings simultaneously. This design flaw becomes particularly problematic when users need to configure related settings like Bluetooth and audio, which should logically work together but are housed in separate sections. The cumbersome navigation creates an inefficient workflow that breaks the user's concentration and productivity. These limitations represent a broader usability crisis in Windows 11, where Microsoft's design choices prioritize visual aesthetics over practical functionality, leaving users with a more frustrating experience than previous Windows versions offered.
Watch clip answer (00:17m)What are some common daily frustrations that computer users experience while working with their devices?
Computer users frequently encounter disruptive dialog boxes that appear unexpectedly while typing, causing accidental confirmations when pressing Enter. These interruptions can lead to unintended actions and user anxiety about what they may have inadvertently agreed to. Beyond dialog boxes, users struggle with Gmail's autocomplete features and Windows 11's complex power settings navigation. These everyday tech grievances create friction in digital workflows and highlight the ongoing challenges between user interface design and practical usability in modern computing environments.
Watch clip answer (00:11m)What are the main frustrations people experience with the current implementation of AI features in everyday technology?
The primary frustration with AI integration stems from the indiscriminate addition of AI features to devices and software without considering user needs or workflow efficiency. Many users find that AI capabilities are being "bolted on" to existing products in a haphazard manner, creating more confusion than providing genuine value. These poorly implemented AI features often complicate rather than simplify user experiences, leading to workflow disruptions and decreased productivity. Instead of enhancing functionality, many AI integrations feel forced and unnecessary, causing users to question whether the technology is truly ready for widespread adoption. The core issue lies in the lack of thoughtful integration - companies are rushing to add AI features without ensuring they genuinely improve the user experience or solve real problems.
Watch clip answer (00:06m)