Economic Policy
Economic policy encompasses the strategies and actions undertaken by governments to influence their nation's economy. It is critical in steering economic growth, controlling inflation, reducing unemployment, and addressing income inequality. Broadly categorized into two main types—**fiscal policy**, which includes government spending and taxation, and **monetary policy**, which focuses on managing the money supply and interest rates—these policies serve as essential tools for economic stabilization and growth. Understanding the mechanisms and implications of these policies is vital, especially in a landscape marked by frequent shifts in global and domestic economic conditions. Recent discussions around economic policy have highlighted concerns over inflation, trade tensions, and the potential for recession, particularly in light of aggressive tariff strategies seen in various countries. These elements underscore a need for careful fiscal management and strategic decision-making to safeguard economic stability. Furthermore, policymakers are increasingly interested in sustainable practices, aimed at bolstering confidence and encouraging investment during periods of uncertainty. With international cooperation becoming vital amidst geopolitical strains, the relevance of sound economic policy frameworks cannot be overstated. As we navigate this complex environment, it remains crucial for both citizens and businesses to understand how economic policies impact their day-to-day lives and long-term prospects.
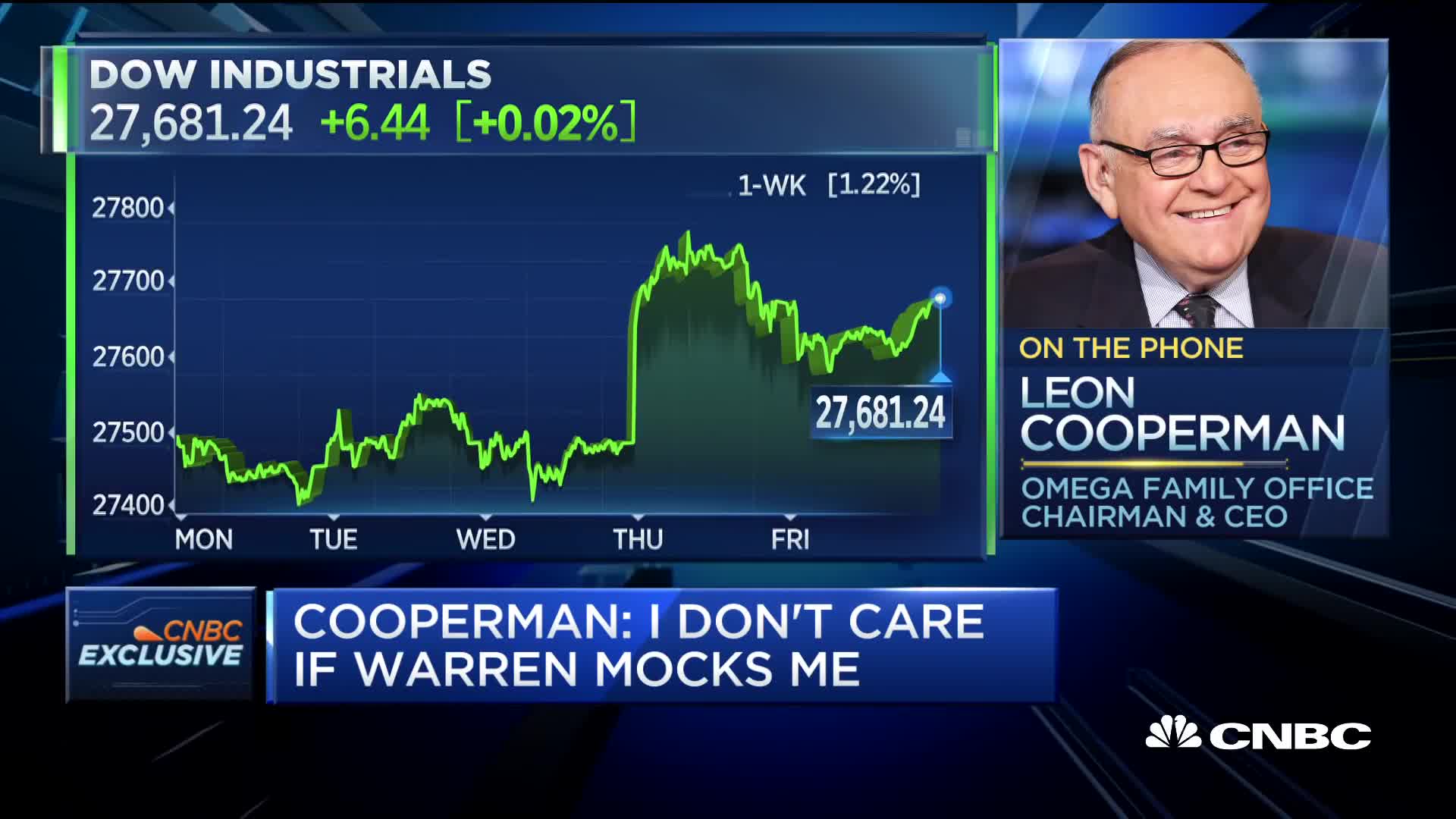
Do you think the S&P 500 is a sell at its current record high, particularly with the upcoming election?
No, Leon Cooperman doesn't believe the S&P 500 is a sell at its current level. He notes that conditions typically preceding market downturns (recession, accelerating inflation, hostile Fed, geopolitical events) are not present. The market appears stable with consumer confidence high, strong retail sales and employment, and decent corporate profits. Cooperman does express concern about two factors: the alarming rate of debt buildup in the country and the political shift to the left. He's also worried about market structure changes, including the elimination of the uptick rule and reduced stabilizing forces. Despite these concerns, he believes the market is 'okay' for the near future.
Watch clip answer (02:51m)How should we leverage AI to benefit economies while managing its potential risks?
AI should be leveraged across multiple domains including robotics, biomedical research, energy technologies, and manufacturing. According to Roubini, proper regulation is essential to ensure we get the best outcomes while mitigating risks like technological unemployment, wealth inequality, and weaponization. Maintaining vibrant economic competition is key to preventing monopolies and encouraging innovation. However, we must address AI's potential negative impacts, including misinformation, job displacement, and social backlash from increased inequality. Societies need to invest in education and skills development to help workers adapt, ensuring that technological advancement benefits everyone rather than just capital owners and highly skilled individuals.
Watch clip answer (06:21m)How should we address the issue of high profits in financial services firms that are considered 'too big to fail'?
Rather than focusing solely on compensation, we need to examine the broader system. Freeland argues that firms benefiting from taxpayer bailouts and implicit government guarantees require special regulatory oversight. When taxpayers rescue financial institutions while facing 10% unemployment, there's a legitimate public interest in preventing future crises. These institutions effectively have a 'taxpayer insurance policy,' which means governments must limit their risky activities to minimize the possibility of future bailouts. This represents a fair exchange: if a firm is deemed too big to fail, it must accept appropriate regulatory constraints to protect the collective good and economic system overall.
Watch clip answer (02:14m)What is the expected impact of Trump's proposed tariffs on prices and jobs?
According to President Trump, while prices might go up somewhat in the short term, the long-term effect would be positive with prices eventually going down. He emphasized that jobs will increase 'tremendously,' creating employment opportunities 'for everybody.' Frank Holland of CNBC explained that tariffs are essentially taxes on imported goods paid by businesses and typically passed on to consumers. However, there's uncertainty about implementation, as the administration is conducting a study due by April 1, suggesting a strategic approach targeting specific trading partners rather than universal tariffs. This tailored approach could potentially boost the US economy and increase foreign investment, leading to the job growth Trump referenced.
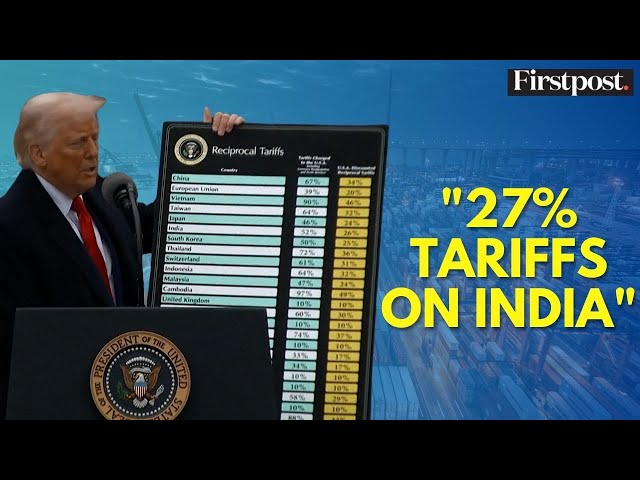
Watch clip answer (02:07m)How does Donald Trump plan to address trade imbalances with countries that charge high tariffs on US goods?
Trump plans to implement reciprocal but discounted tariffs against countries charging high rates to the US. For example, against China's 67% tariff, Trump would charge 34%; against the EU's 39%, he would charge 20%; and against Vietnam's 90%, he would implement a 46% tariff. This approach applies to numerous countries including Japan (24% instead of 46%) and Cambodia (49% instead of 97%). Trump emphasizes that his administration would consistently charge less than what other nations impose on the US, creating what he considers a fairer trade balance.
Watch clip answer (04:42m)How do Trump's 25% tariffs on Chinese imports protect American automakers?
Trump's 25% tariff on Chinese imports protects American automakers by reducing the price gap between Chinese and American vehicles. By adding approximately $8,750 to a $35,000 Chinese car (making it $43,750), the tariff narrows the difference with American-made vehicles (priced around $45,000) to only $1,250. This smaller price gap gives American manufacturers a much better chance to compete against Chinese imports. The tariff strategy aims to prevent China from flooding the US market with cheaper vehicles, ultimately helping to preserve American manufacturing jobs and domestic production capacity in the automotive sector.
Watch clip answer (00:31m)