Economic Policy
Economic policy encompasses the strategies and actions undertaken by governments to influence their nation's economy. It is critical in steering economic growth, controlling inflation, reducing unemployment, and addressing income inequality. Broadly categorized into two main types—**fiscal policy**, which includes government spending and taxation, and **monetary policy**, which focuses on managing the money supply and interest rates—these policies serve as essential tools for economic stabilization and growth. Understanding the mechanisms and implications of these policies is vital, especially in a landscape marked by frequent shifts in global and domestic economic conditions. Recent discussions around economic policy have highlighted concerns over inflation, trade tensions, and the potential for recession, particularly in light of aggressive tariff strategies seen in various countries. These elements underscore a need for careful fiscal management and strategic decision-making to safeguard economic stability. Furthermore, policymakers are increasingly interested in sustainable practices, aimed at bolstering confidence and encouraging investment during periods of uncertainty. With international cooperation becoming vital amidst geopolitical strains, the relevance of sound economic policy frameworks cannot be overstated. As we navigate this complex environment, it remains crucial for both citizens and businesses to understand how economic policies impact their day-to-day lives and long-term prospects.
What challenges does the Commerce Secretary face regarding the tariff study announced by the Trump administration?
Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick faces the massive task of examining trading relationships with approximately 200 countries worldwide. This comprehensive study will require assessing existing tariffs and trade arrangements with each nation to evaluate reciprocity in these relationships. The administration plans to use this analysis as a foundation for future trade negotiations, as evidenced by meetings with world leaders like the Prime Minister of India. This process appears to be gaining momentum, with more international leaders expected to visit Washington to discuss trade matters directly with the President.
Watch clip answer (00:20m)Why does the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) experience such extreme poverty despite its vast mineral wealth?
The DRC's poverty stems from two major factors. First, its brutal colonial history under Belgian rule, which pillaged resources and brutalized the population for nearly a century, creating lasting legacies that continue to impact development. Second, the country's challenging natural geography severely constrains economic growth and trade. Despite possessing mineral reserves worth approximately $24 trillion including cobalt, coltan, copper, gold, diamonds, and lithium, the DRC has a nominal GDP per capita of just $702—the 11th lowest globally. This stark contrast between extreme wealth and poverty illustrates how historical exploitation and geographical constraints have trapped the second-largest country in Africa in chronic underdevelopment.
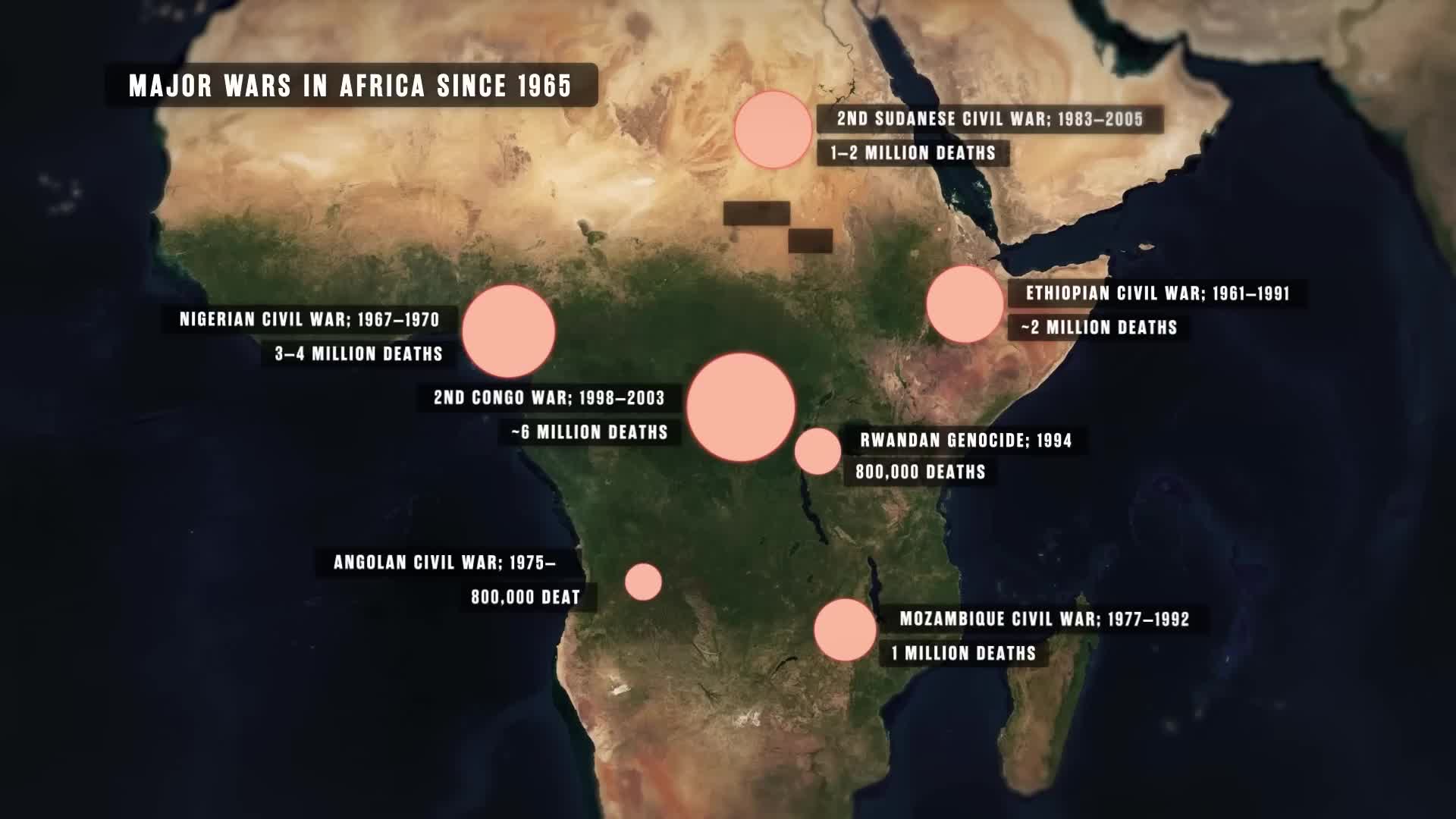
Watch clip answer (01:56m)How has the geography of Africa contributed to the continent's chronic poverty?
The geography of Africa has severely handicapped its development throughout history, acting as a major contributor to the continent's chronic poverty. Geographical barriers such as extensive deserts, non-navigable rivers, and lack of natural harbors have created significant obstacles to trade and economic growth. These geographical limitations have held back Africa's peoples for generations, from ancient times through the present day. Despite being rich in natural resources, these geographical constraints, combined with historical challenges like colonialism and corruption, have created persistent socioeconomic difficulties that continue to impact development across the continent.
Watch clip answer (00:21m)Why is Africa so poor despite being rich in natural resources?
Africa remains the poorest continent despite possessing extraordinary mineral wealth, including 50% of all gold ever mined and the world's largest reserves of diamonds, platinum, and critical minerals like cobalt. This paradox stems from historical factors like colonialism and ongoing neocolonial exploitation, coupled with geographical challenges that hinder trade and development. The Democratic Republic of Congo illustrates this contradiction perfectly - it contains an estimated $24 trillion in mineral resources, yet its entire GDP in 2023 was only $66 billion, demonstrating how resource wealth fails to translate into economic prosperity for African nations.
Watch clip answer (02:28m)How has Singapore emerged as a global economic powerhouse despite its small size?
Despite its limited geographic size, Singapore has transformed into a remarkable economic force with a nominal GDP of US$548 billion as of 2025, making it the world's 26th largest economy. This places Singapore far higher in economic rankings than its physical dimensions would suggest, with an economy roughly equivalent to Thailand's despite having only 1/11th of Thailand's population. Singapore ranks as the 10th largest economy on the Asian continent (excluding Russia), despite being only the 36th most populous Asian country. This economic colossus has defied its physical limitations, demonstrating how strategic economic policies can elevate a small island nation into a global financial powerhouse.
Watch clip answer (00:54m)What were Trump's goals for American territorial expansion and how did he propose to achieve them?
During a press conference at Mar-a-Lago in early January, Donald Trump explicitly outlined his territorial expansion goals, claiming the Panama Canal should never have been ceded to Panama, alleging without evidence that it was operated by China and needed for American economic security. He also expressed interest in acquiring Greenland for national security purposes, questioning Denmark's legal right to the territory. Trump threatened to impose high-level tariffs on Denmark if they refused to cooperate in relinquishing Greenland. When pressed by a reporter, he notably refused to rule out using the US Military to acquire either Greenland or the Panama Canal, suggesting he was willing to consider forceful measures if diplomatic or economic pressure failed to achieve his territorial ambitions.
Watch clip answer (00:44m)