Economic Inequality
Economic inequality refers to the uneven distribution of income, wealth, and resources among individuals or groups within society. It encompasses a variety of disparities, including income inequality, the wealth gap, and economic disparity, which are perpetuated by factors such as education, race, gender, and economic policies. Recent trends indicate that a significant portion of the global population, particularly the top 1% and 0.1%, captures an increasing share of global wealth, engendering profound consequences for social cohesion and economic growth. Despite some nations making strides to lessen inequality between them, the internal inequality within many countries is on the rise, signaling the need for urgent policy interventions to address these challenges effectively. The importance of understanding economic inequality has never been greater, especially in the context of evidence showing that excessive wealth gaps can lead to social unrest, political polarization, and diminished trust in institutions. Studies indicate that two-thirds of the world’s population resides in areas experiencing heightened income inequality, highlighting how technological advancements and globalization often favor wealth accumulation among the richest, ultimately impacting middle and low-income groups. A focus on addressing economic disparities is crucial, as failing to do so can undermine societal progress and exacerbate social divides. Policymakers are being called to action to create more equitable systems through progressive taxation, improved access to education, and robust social safety nets, in hopes of fostering inclusive growth amid a rapidly changing global landscape.
How might the modernization of the tax system affect low-income Americans?
Low-income Americans who rely on prompt tax refunds could face significant challenges due to potential disruptions in the tax system. According to financial experts, while there's bipartisan agreement that modernizing tax returns for greater efficiency is good policy, implementing changes too quickly—especially during tax filing season—risks harming those who depend on timely refunds the most. The situation is further complicated by the fact that while the top 1% of taxpayers are responsible for one quarter of all missing tax revenue, it's often ordinary Americans who suffer from system inefficiencies. This underscores the delicate balance required when reforming tax processes to ensure that vulnerable populations don't experience delays in receiving their much-needed tax returns.
Watch clip answer (00:35m)What does Mitch Landrieu criticize about Donald Trump's priorities as president?
Mitch Landrieu criticizes Trump for focusing on foreign policy issues rather than addressing domestic concerns affecting working Americans. He points out that while economic indicators for working men and women have worsened under Trump, the former president is preoccupied with international matters like 'giving away Ukraine to Russia' and antagonizing allies including Canada, Mexico, and European nations. Landrieu argues that Trump's failure to concentrate on the American people is particularly problematic. He emphasizes that instead of addressing crucial domestic issues, Trump is alienating traditional allies who have historically stood 'shoulder to shoulder' with America, even telling European friends who fought alongside Americans at Normandy to 'take a hike.'
Watch clip answer (00:29m)How has the destruction of the Sennaar sugar factory affected local farmers in Sudan?
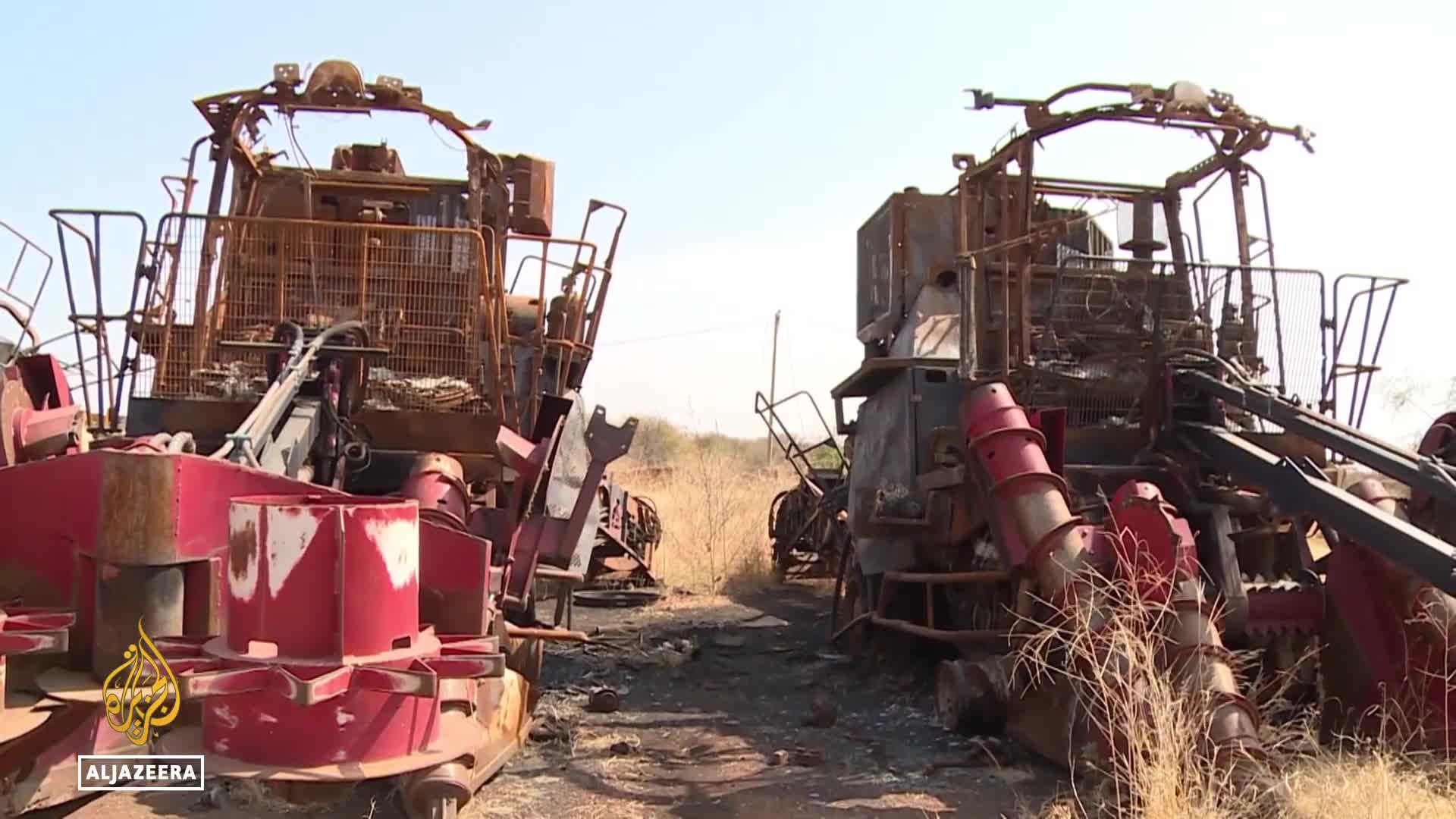
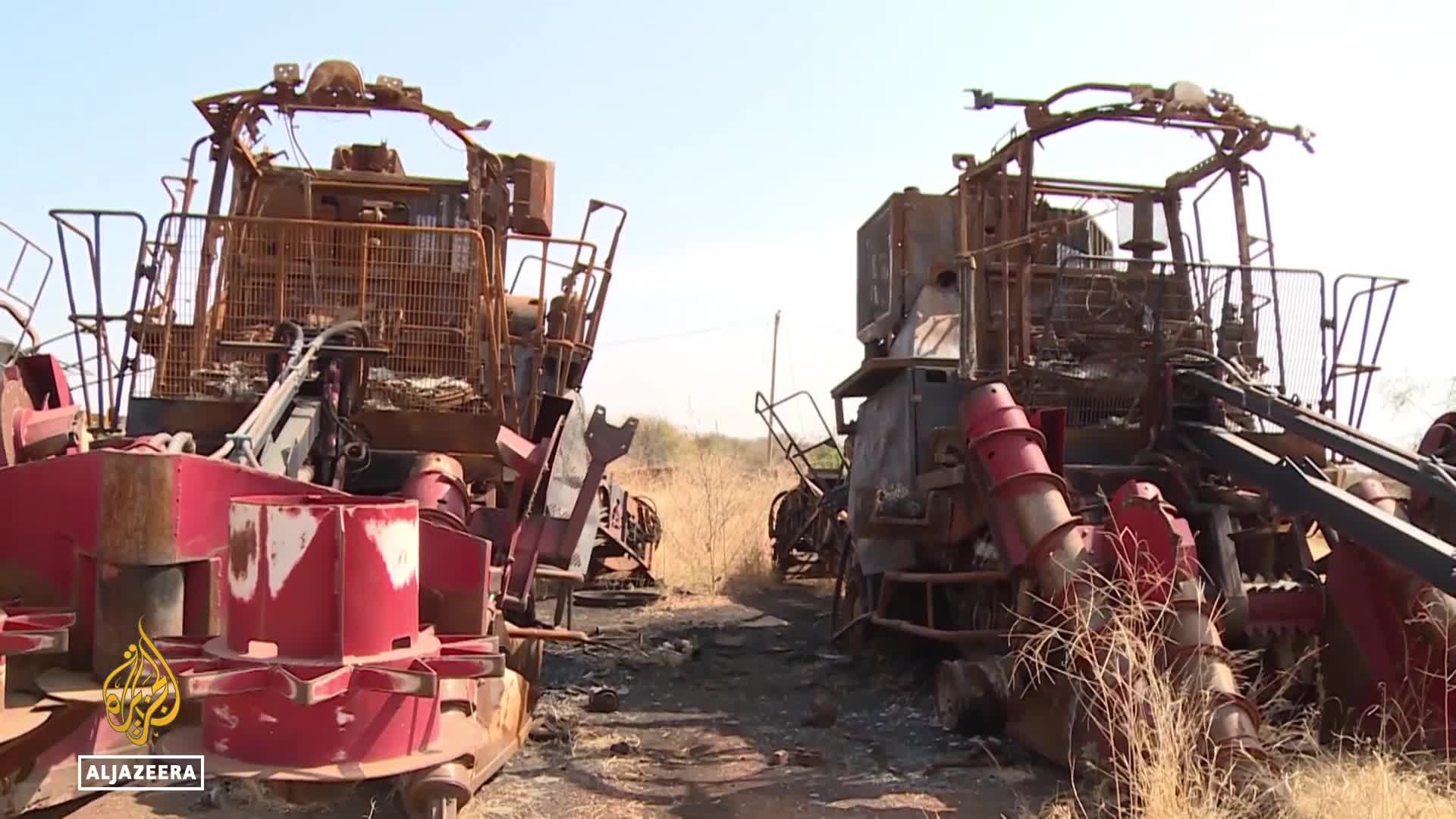
The destruction of the Sennaar sugar factory has devastated the local farming community, directly impacting their livelihoods and welfare. According to Uncle Khidr, a farmer living near the factory, the community's lifestyle was intrinsically linked to the sugar production facility, which produced sugar that was "much sweeter," "much better," and "more concentrated" than imports. When the factory was destroyed during recent conflicts, the farmers' economic stability collapsed alongside it. This impact extends beyond economics to cultural significance, as sugar plays a central role in Sudanese daily life, with many Sudanese like Uncle Khidr consuming their coffee with cups "nearly half full of sugar."
Watch clip answer (00:30m)How has the destruction of the sugar factory affected the local farming community in Sudan?
The destruction of the sugar factory has devastated the local farming community, completely dismantling their livelihoods and way of life. As Uncle Khidr and other farmers near the Sennaar factory explain, their welfare and lifestyle were directly linked to the sugar production facility. When the factory was destroyed amid the ongoing conflict, farmers lost not only their economic stability but also their connection to traditional practices. The community takes pride in their locally produced sugar, which they describe as 'much sweeter' and 'more concentrated' than imports. This crisis represents more than just economic hardship—it's the loss of a cultural cornerstone in a society where sweeteners remain a dietary staple.
Watch clip answer (00:30m)What is Sudan's current sugar production and consumption situation?
Sudan's annual sugar consumption amounts to approximately 1 million tons, but the country is heavily reliant on imports to meet this demand despite having agricultural potential. Most sugar is now imported from various countries including Brazil and Cuba, as Sudan has never achieved self-sufficiency in sugar production. Even when local sugar factories were operational, Sudan still needed to import sugar to satisfy domestic needs. The situation has worsened due to ongoing conflict and economic turmoil, leaving many sugar factories defunct and farmers without livelihoods tied to domestic production, further deepening the country's dependence on foreign sugar sources.
Watch clip answer (00:18m)Who contributes to Social Security in America?
Every single person with a job in America contributes to Social Security through their paychecks. This universal contribution applies to workers across all economic levels, including the wealthiest Americans. No employed individual is exempt from this system. Regardless of occupation or income status, each paycheck received by American workers includes a contribution to Social Security. This creates a comprehensive system where all participants in the workforce support this crucial program that serves as a fundamental element of America's social safety net for over 70 million people.
Watch clip answer (00:09m)