Economic Growth
Economic growth is a critical metric that reflects the sustained increase in the production of goods and services within an economy. Typically measured by the rise in Gross Domestic Product (GDP) or GDP per capita, economic growth is integral to enhancing living standards and alleviating poverty. Recent evaluations indicate that global GDP growth is expected to stabilize in the range of 2.6% to 3.3%, amid numerous challenges such as geopolitical tensions and inflationary pressures. Understanding economic growth is not only essential for policymakers and economists but also for citizens as it influences job creation, income levels, and overall societal progress. Key drivers of economic growth include investment in physical capital, growth in the labor force, and advancements in technology, which together facilitate a nation's ability to expand its output effectively. Moreover, various economic theories, including endogenous growth theory, emphasize the role of innovation and human capital in achieving long-term growth. Additionally, the ongoing discussions about sustainable economic development highlight the importance of creating growth strategies that not only boost GDP but also are equitable and environmentally conscious. As nations work towards sustainable solutions, comprehending the dynamics of economic growth becomes increasingly pertinent amidst continual global shifts in economic conditions and policies.
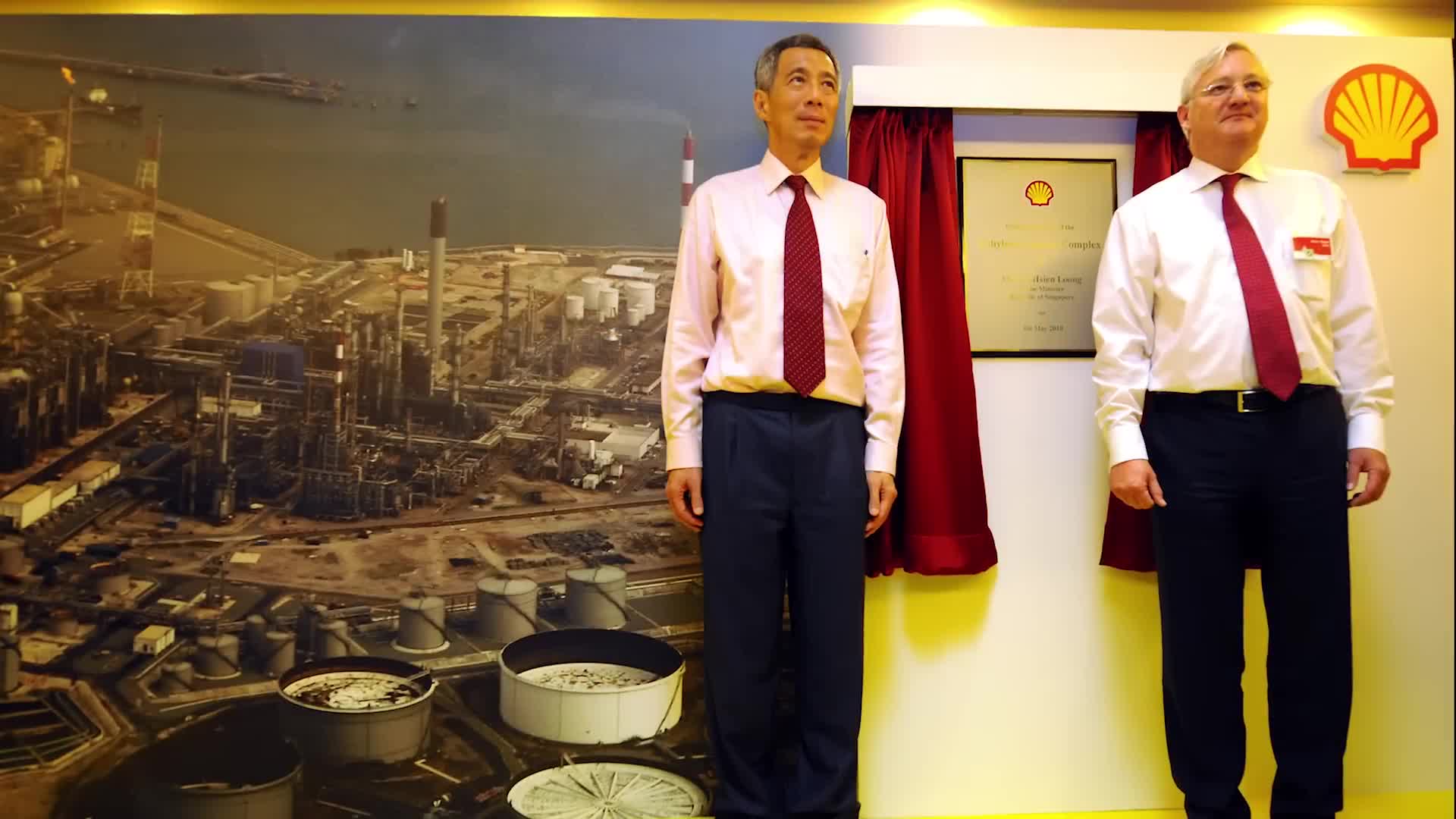
Why is Singapore considered the largest maritime refueling port in the world?
Singapore holds the distinction of being the world's largest refueling port for ships, significantly outperforming its competitors in the maritime industry. The city-state supplies approximately five times more fuel to the maritime industry compared to Rotterdam in the Netherlands, which ranks as the second largest refueling port globally. This dominance in the maritime refueling sector reflects Singapore's strategic position at the Strait of Malacca, which has enabled it to evolve into a crucial hub for global maritime trade. With its highly developed infrastructure and business-friendly policies, Singapore has established itself as an indispensable player in international shipping and maritime services.
Watch clip answer (00:13m)How has Singapore emerged as a global economic powerhouse despite its small size?
Despite its limited geographic size, Singapore has transformed into a remarkable economic force with a nominal GDP of US$548 billion as of 2025, making it the world's 26th largest economy. This places Singapore far higher in economic rankings than its physical dimensions would suggest, with an economy roughly equivalent to Thailand's despite having only 1/11th of Thailand's population. Singapore ranks as the 10th largest economy on the Asian continent (excluding Russia), despite being only the 36th most populous Asian country. This economic colossus has defied its physical limitations, demonstrating how strategic economic policies can elevate a small island nation into a global financial powerhouse.
Watch clip answer (00:54m)Can financial incentives fix China's population crisis?
The effectiveness of China's financial incentives to address its population crisis remains questionable. While local initiatives like cash rewards for newlyweds are being implemented to counter declining marriage and birth rates, the underlying issues appear more complex than monetary solutions alone can address. As noted in the clip, the Chinese government's political and economic ambitions are directly linked to resolving this demographic challenge. The success of these incentives will likely depend on how they address broader concerns such as rising childcare costs and sluggish economic growth that contribute to young people's reluctance to marry and have children.
Watch clip answer (00:13m)Why is China facing declining marriage and birth rates, and what initiatives are being taken to address this issue?
China faces declining interest in marriage and family formation primarily due to the high costs of childcare and education. Economic challenges, including sputtering growth in recent years, have created employment difficulties for university graduates, further discouraging young couples from starting families. This situation has contributed to the country's declining population. In response, the government has launched initiatives to encourage young couples to marry and have children, aiming to boost population growth. These efforts represent China's attempt to counter demographic challenges that could affect its economic future.
Watch clip answer (00:29m)What is China doing to address declining marriage and birth rates?
China is implementing financial incentives to boost declining marriage and birth rates amid population concerns. Local authorities in Luliang, Shanxi Province are offering cash rewards of 1500 yuan to newlywed couples, with additional subsidies for each registered child born. These measures directly respond to the country's alarming 20% drop in marriages during 2024 and sustained population decrease. The government is particularly concerned about the shrinking population and is actively encouraging young people to marry and have children despite rising economic pressures and high costs associated with childcare and education.
Watch clip answer (00:13m)How are China's political and economic ambitions connected to its marriage and birth rate crisis?
China's political and economic ambitions are directly linked to its declining marriage registrations and birth rates. The government's strategic goals depend on maintaining a robust population to sustain economic growth and global influence. In response to the alarming 20% drop in marriage rates and continued population decline in 2024, authorities have implemented financial incentives such as the cash reward scheme in Luliang, where couples receive subsidies for each child registered. These measures reflect China's recognition that its national ambitions are threatened by demographic challenges stemming from economic pressures, rising childcare costs, and job insecurity faced by young adults.
Watch clip answer (00:07m)