Economic Growth
Economic growth is a critical metric that reflects the sustained increase in the production of goods and services within an economy. Typically measured by the rise in Gross Domestic Product (GDP) or GDP per capita, economic growth is integral to enhancing living standards and alleviating poverty. Recent evaluations indicate that global GDP growth is expected to stabilize in the range of 2.6% to 3.3%, amid numerous challenges such as geopolitical tensions and inflationary pressures. Understanding economic growth is not only essential for policymakers and economists but also for citizens as it influences job creation, income levels, and overall societal progress. Key drivers of economic growth include investment in physical capital, growth in the labor force, and advancements in technology, which together facilitate a nation's ability to expand its output effectively. Moreover, various economic theories, including endogenous growth theory, emphasize the role of innovation and human capital in achieving long-term growth. Additionally, the ongoing discussions about sustainable economic development highlight the importance of creating growth strategies that not only boost GDP but also are equitable and environmentally conscious. As nations work towards sustainable solutions, comprehending the dynamics of economic growth becomes increasingly pertinent amidst continual global shifts in economic conditions and policies.
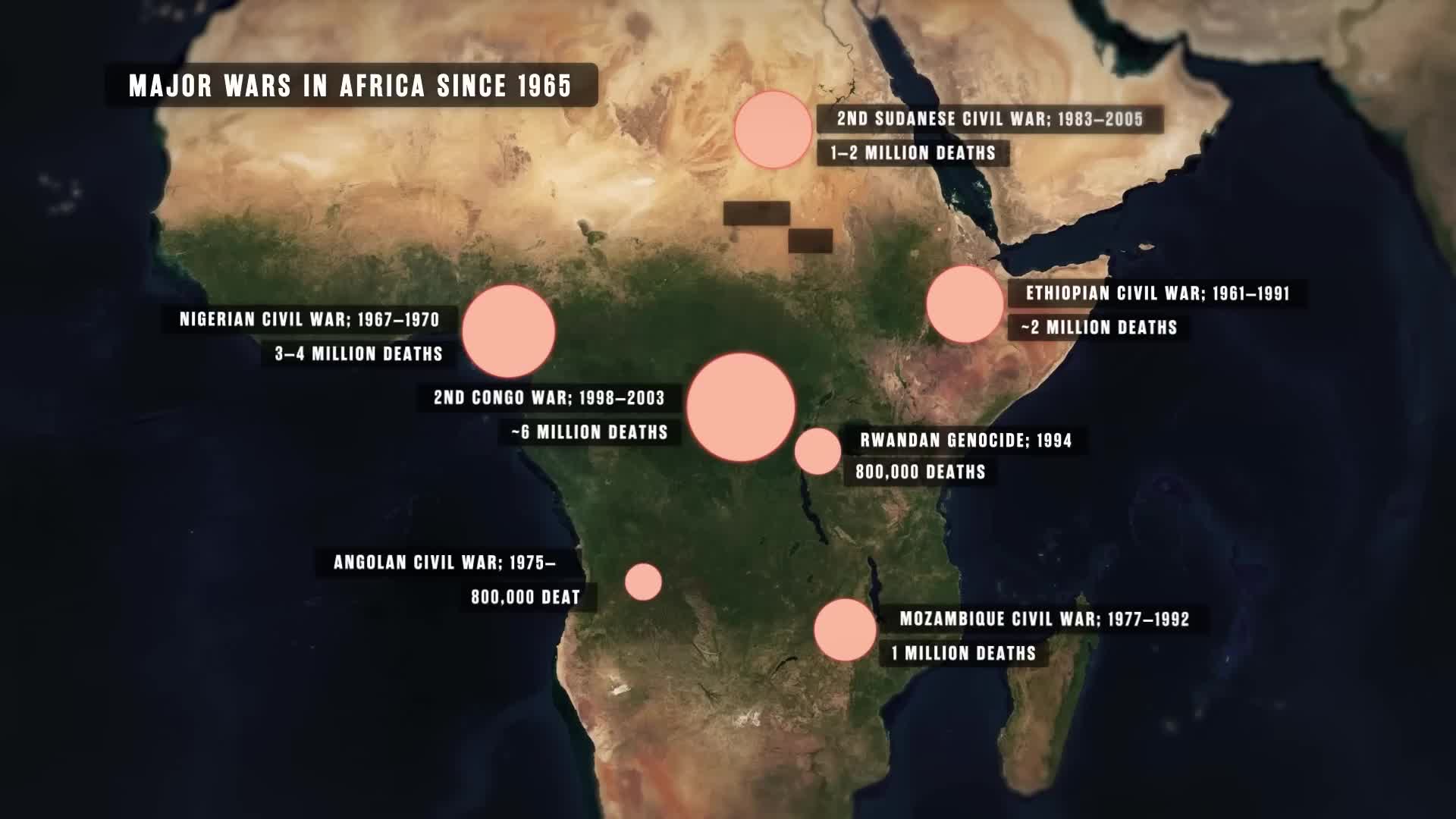
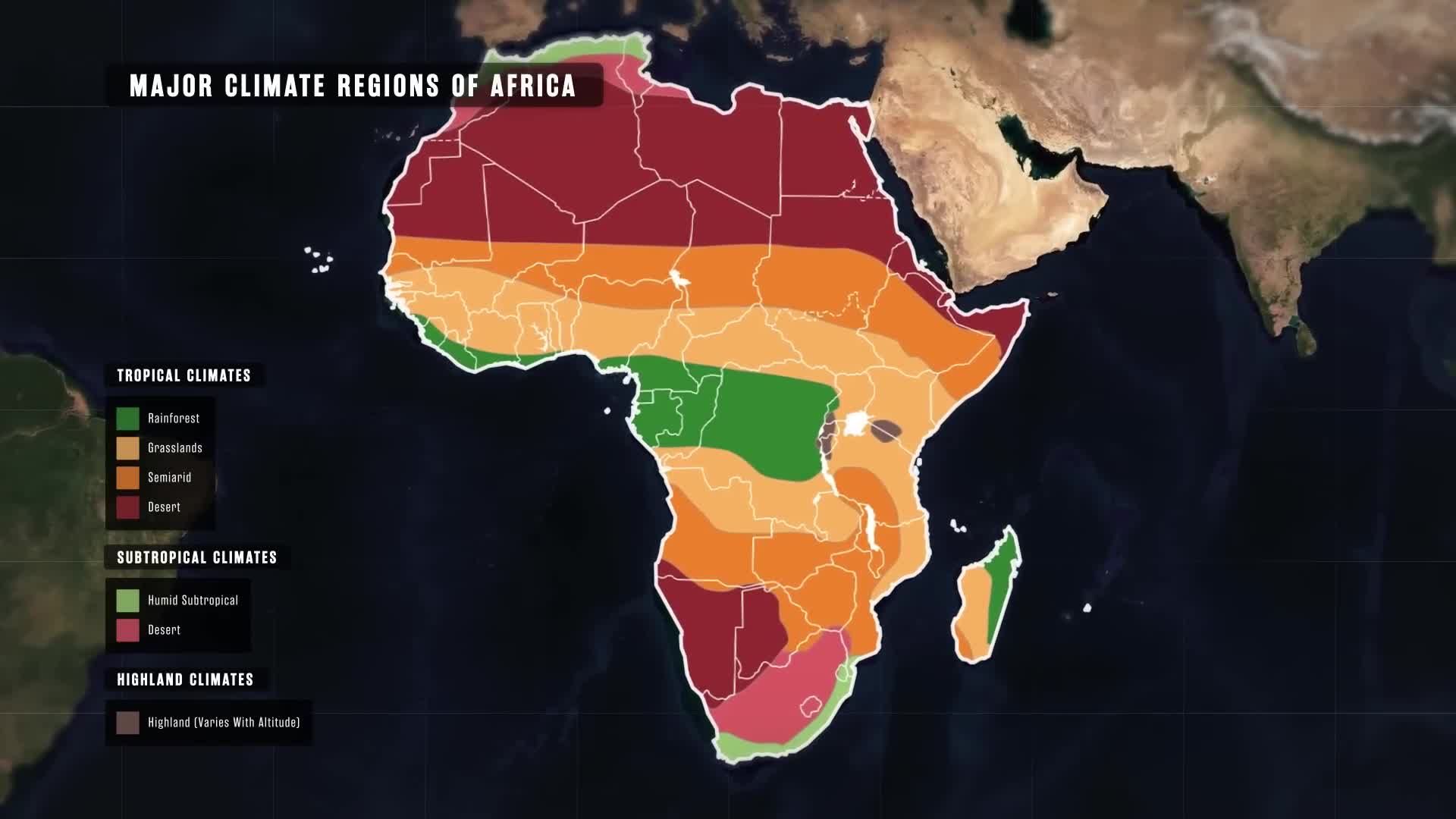
How has the geography of Africa contributed to the continent's chronic poverty?
The geography of Africa has severely handicapped its development throughout history, acting as a major contributor to the continent's chronic poverty. Geographical barriers such as extensive deserts, non-navigable rivers, and lack of natural harbors have created significant obstacles to trade and economic growth. These geographical limitations have held back Africa's peoples for generations, from ancient times through the present day. Despite being rich in natural resources, these geographical constraints, combined with historical challenges like colonialism and corruption, have created persistent socioeconomic difficulties that continue to impact development across the continent.
Watch clip answer (00:21m)Why is Africa so poor despite being rich in natural resources?
Africa remains the poorest continent despite possessing extraordinary mineral wealth, including 50% of all gold ever mined and the world's largest reserves of diamonds, platinum, and critical minerals like cobalt. This paradox stems from historical factors like colonialism and ongoing neocolonial exploitation, coupled with geographical challenges that hinder trade and development. The Democratic Republic of Congo illustrates this contradiction perfectly - it contains an estimated $24 trillion in mineral resources, yet its entire GDP in 2023 was only $66 billion, demonstrating how resource wealth fails to translate into economic prosperity for African nations.
Watch clip answer (02:28m)How does Africa's geography hinder its trade and economic connectivity?
Africa's geography creates two major barriers to trade. First, the Sahara Desert—comparable in size to the entire United States—effectively functions as an impassable ocean of sand that has historically isolated sub-Saharan Africa from Eurasia and North Africa. Even today, there are only a handful of highways crossing it and no railways connecting north to south. Second, Africa's coastlines are remarkably smooth, lacking the natural harbors essential for maritime commerce. Despite being nearly four times larger than Europe, Africa's coastline is about six times shorter due to its smoothness. This severe shortage of usable natural harbors has significantly handicapped Africans' ability to conduct maritime trade throughout history, limiting economic development and cultural exchange.
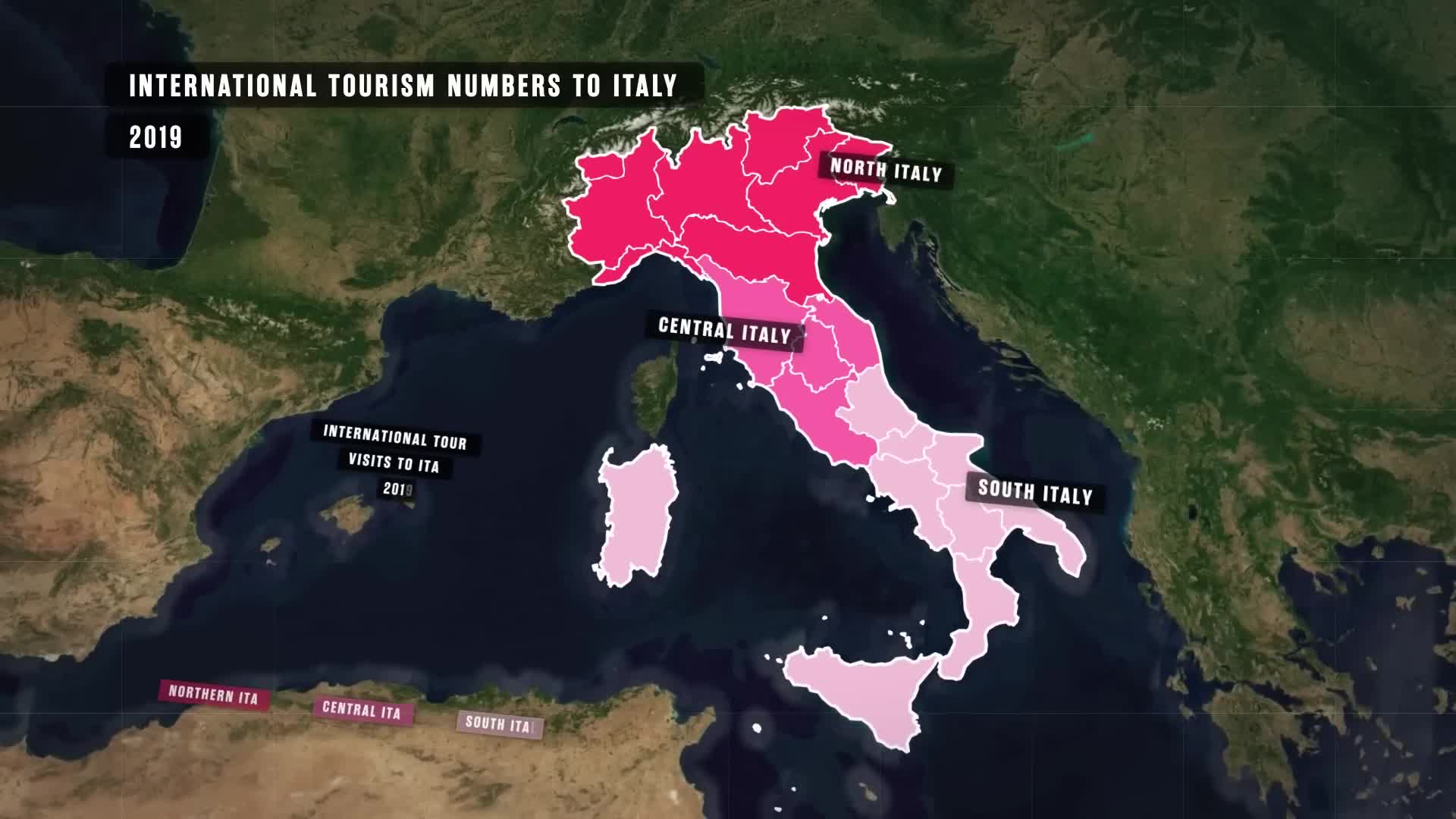
Watch clip answer (03:25m)What are the key variables that measure the development disparity between northern and southern Italy?
Two crucial variables measuring the north-south divide in Italy are Human Development Index (HDI) scores and GDP per capita. The HDI, measured on a 0-1 scale by the United Nations, considers healthcare access, education, income levels, and living conditions. Maps show a clear gradient: the further south you go in Italy, the lower the development becomes. While southern regions like Calabria and Sicily score around 0.859, which appears underdeveloped by Western European standards, these scores remain relatively high globally, comparable to Argentina, Chile, or Turkey, and above the global average.
Watch clip answer (01:18m)How does Southern Italy's tourism performance compare to other Mediterranean destinations?
Southern Italy significantly underperforms compared to similar Mediterranean destinations. Barcelona attracts nearly twice as many tourists annually as Naples (Southern Italy's largest city), while the Spanish Balearic Islands alone draw more than half the tourists of all Southern Italy combined, despite their much smaller geographic size. This disparity highlights that Southern Italy's tourism potential is severely underutilized. The region currently receives only about 15% of Italy's total tourist traffic, while Northern Italy captures 60%. This suggests considerable growth opportunities for Southern Italy's tourism sector if the correct development and promotion strategies are implemented.
Watch clip answer (00:27m)How did Singapore transform from a poor nation to a wealthy global economic powerhouse in just 60 years?
Singapore transformed from a deeply impoverished nation with a GDP per capita of just $511 in 1965 to one of the world's wealthiest cities with a current GDP per capita of $89,000. At independence, the country faced 14% unemployment, 70% of people lived in overcrowded conditions, half the population was illiterate, and it had zero natural resources or freshwater. Despite these humble beginnings, through strategic governance, focus on education, and attracting foreign investment, Singapore evolved within a single human lifetime to become the world's third most significant global financial center, demonstrating one of history's most dramatic national economic transformations.
Watch clip answer (01:25m)