Economic Development
Economic development is a comprehensive process focused on enhancing the economic well-being and quality of life of individuals and communities. It transcends mere economic growth, which is typically measured by increases in GDP, by emphasizing sustainable practices, infrastructure improvements, job creation, and empowerment through education and skill development. The relevant strategies for economic development often include tailored initiatives such as business incentive programs, community growth planning, and comprehensive economic development strategies that align with the unique characteristics and needs of local populations. Recently, the global economic landscape has been characterized by slowing growth and persistent uncertainty, factors that have considerable implications for economic development efforts. While advanced economies face stagnation and threats of stagflation, emerging markets strive to adopt alternative development models that leverage local resources and inclusive policies. The shift towards a more mercantilist international economy, where trade and fiscal policies dominate over monetary solutions, further complicates the dynamics of economic development. In this context, it is essential for policymakers and economic development professionals to adapt strategies that not only create wealth but also ensure that economic benefits are distributed equitably among their communities. Continued emphasis on resilient economic frameworks, designed to withstand volatility, is critical in navigating modern challenges and fostering prosperity for all.
What is the current state of China's property income growth?
China's property income growth has reached its lowest level in over a decade, with per capita net property income growing by only 2.2% in 2024 - the slowest pace since 2014. This represents a consistent downward trend in the growth rate that has been ongoing since 2019, with 2021 being the only exception. This record low growth highlights the continuing slump in China's real estate sector, which has significant implications for the broader economy. Official data confirms this persistent decline, reflecting the challenges facing one of China's most important economic pillars.
Watch clip answer (00:22m)How is China's real estate decline affecting the middle class?
China's underperforming real estate market is significantly impacting its middle class population. Property income, which forms a crucial component of household earnings, is declining, indicating asset depreciation for numerous homeowners across the country. This financial setback is particularly concerning as property has traditionally been a key wealth-building mechanism for China's middle class. The diminishing returns from real estate are contributing to weakened consumer confidence and creating financial strain on middle-class households who have invested substantially in property.
Watch clip answer (00:14m)How does Africa's geography hinder trade and economic development?
Africa's unique elevation profile creates significant barriers to trade. Unlike Europe, most of Africa features high plateaus that rapidly descend to sea level near the coasts, forming steep escarpments. These create narrow coastal plains (often just dozens of kilometers wide) with limited hinterlands for development. Additionally, Africa lacks navigable rivers connecting to oceans, eliminating possibilities for maritime riverine trade between the interior and global markets. This geographical isolation, combined with few natural harbors, has historically prevented efficient trade connections and contributed substantially to the continent's economic challenges.
Watch clip answer (01:33m)Why does the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) experience such extreme poverty despite its vast mineral wealth?
The DRC's poverty stems from two major factors. First, its brutal colonial history under Belgian rule, which pillaged resources and brutalized the population for nearly a century, creating lasting legacies that continue to impact development. Second, the country's challenging natural geography severely constrains economic growth and trade. Despite possessing mineral reserves worth approximately $24 trillion including cobalt, coltan, copper, gold, diamonds, and lithium, the DRC has a nominal GDP per capita of just $702—the 11th lowest globally. This stark contrast between extreme wealth and poverty illustrates how historical exploitation and geographical constraints have trapped the second-largest country in Africa in chronic underdevelopment.
Watch clip answer (01:56m)How does Africa's geography impact trade opportunities compared to other continents?
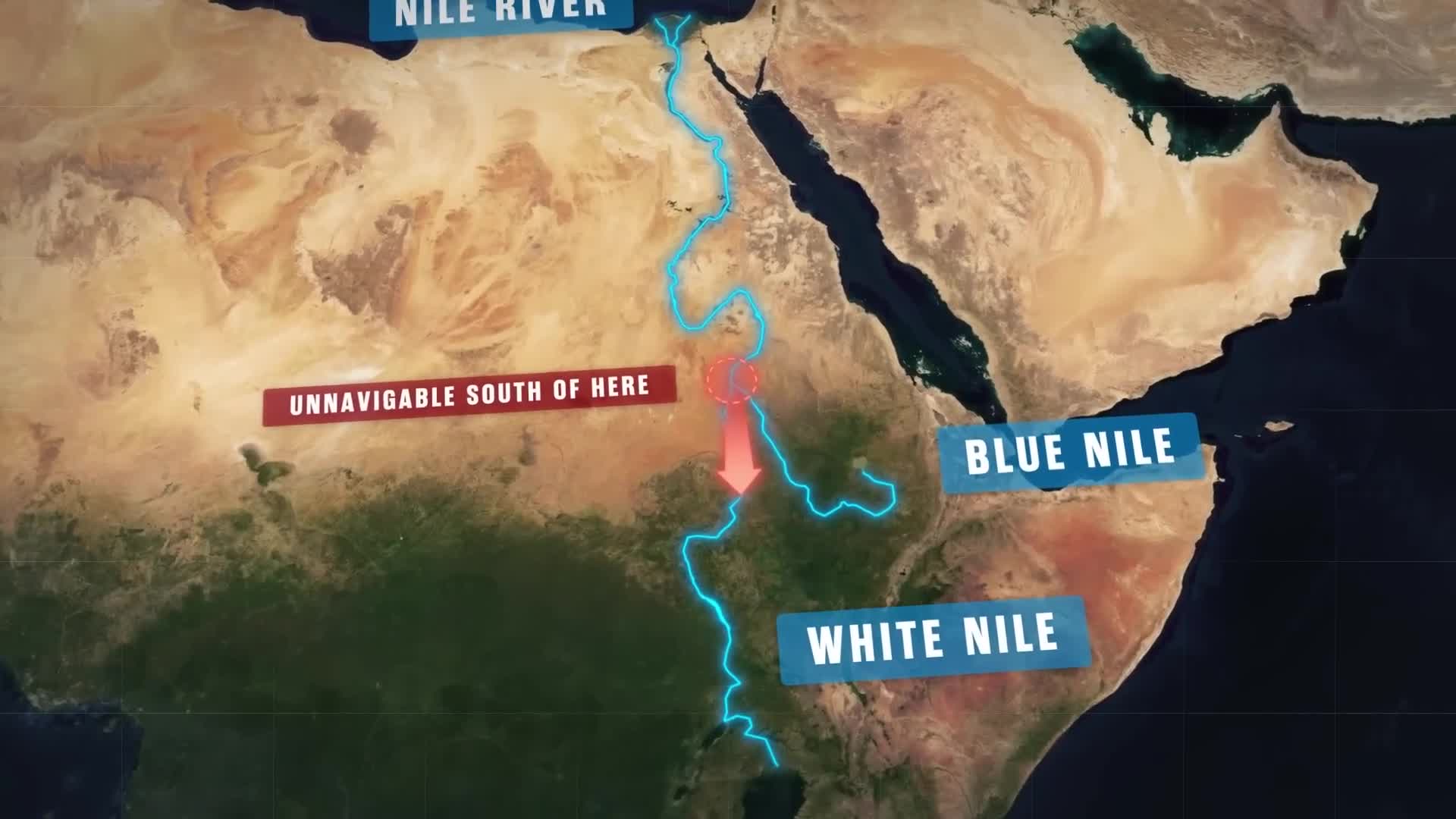
Africa faces severe geographical disadvantages for trade compared to other continents. While China's Yangtze River and North America's Mississippi Basin offer extensive navigable waterways connecting interior regions to oceans, Africa lacks such natural transportation networks. The Nile River, Africa's only significant navigable waterway, becomes unnavigable beyond Khartoum in Sudan due to rapids, preventing Sub-Saharan African merchants from efficient sea access. This geographical constraint forces African merchants to use expensive land transportation around unnavigable river sections, significantly increasing costs compared to their European, Asian, and American counterparts. When combined with Africa's lack of natural harbors and the barrier of the Sahara Desert, these factors have historically isolated Sub-Saharan Africa from global trade opportunities, contributing to the continent's economic challenges.
Watch clip answer (02:36m)How has the geography of Africa contributed to the continent's chronic poverty?
The geography of Africa has severely handicapped its development throughout history, acting as a major contributor to the continent's chronic poverty. Geographical barriers such as extensive deserts, non-navigable rivers, and lack of natural harbors have created significant obstacles to trade and economic growth. These geographical limitations have held back Africa's peoples for generations, from ancient times through the present day. Despite being rich in natural resources, these geographical constraints, combined with historical challenges like colonialism and corruption, have created persistent socioeconomic difficulties that continue to impact development across the continent.
Watch clip answer (00:21m)