Climate Change
Climate change refers to significant and long-term alterations in temperature, wind patterns, and precipitation on Earth, primarily driven by human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, industrial processes, and agricultural practices. This phenomenon has led to a global temperature increase of approximately 1.1°C since the pre-industrial era, as greenhouse gases accumulate in the atmosphere. The effects of climate change are vast, influencing everything from rising sea levels and melting ice sheets to more frequent extreme weather events such as hurricanes, heatwaves, floods, and droughts. Understanding the impacts of climate change is crucial for taking informed action and developing effective renewable energy solutions and carbon footprint reduction strategies. The urgency to address climate change has gained significant momentum as global temperatures approach critical thresholds. Recent studies indicate that if current trends continue, there is a 70% likelihood that the average warming for the near future will exceed 1.5°C, which is a crucial limit outlined in international climate agreements like the Paris Agreement. The consequences of unchecked climate change pose risks not only to ecosystems but also to human health, food security, and economic stability. With reports highlighting alarming rates of progress—or lack thereof—across various climate indicators, effective actions such as the implementation of renewable energy solutions and comprehensive climate finance must be prioritized to mitigate the ongoing crisis. As nations strive to meet ambitious climate targets, the need for immediate and coordinated action has never been more critical.
What role does bamboo play in sustainability and construction?
Bamboo is increasingly becoming the backbone of construction and sustainability through innovative applications. Scientists in China have pioneered technologies to enhance bamboo's strength and durability for large-scale infrastructure, as demonstrated in the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge. Despite appearing woody, bamboo is actually a grass with a strength-to-weight ratio surpassing certain steel alloys. Beyond construction, bamboo significantly contributes to fighting climate change by absorbing nearly 50% more carbon dioxide than typical trees. India introduced the world's first 200-meter bamboo crash barrier in Maharashtra in 2023, which underwent rigorous testing and achieved top safety ratings. These barriers offer 50-70% recycling value, higher than traditional steel barriers at 30-50%, setting new standards for sustainable road safety solutions.
Watch clip answer (02:39m)How is bamboo being utilized in modern construction and sustainability efforts?
Bamboo is increasingly becoming the backbone of construction and sustainability, with scientists in China developing advanced technologies to enhance its strength and durability for large-scale infrastructure projects. A notable example is the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge, where bamboo composite panels have successfully withstood harsh conditions including sunlight, typhoons, and seawater exposure for six years. Despite its woody appearance, bamboo is actually a grass with a strength-to-weight ratio surpassing certain steel alloys. It absorbs nearly 50% more carbon dioxide than typical trees, making it environmentally superior. India has also pioneered the world's first 200-meter bamboo crash barrier on a highway in Maharashtra, which achieved top fire safety ratings and proved its resilience in high-impact situations while offering 50-70% recycling value compared to steel barriers' 30-50%.
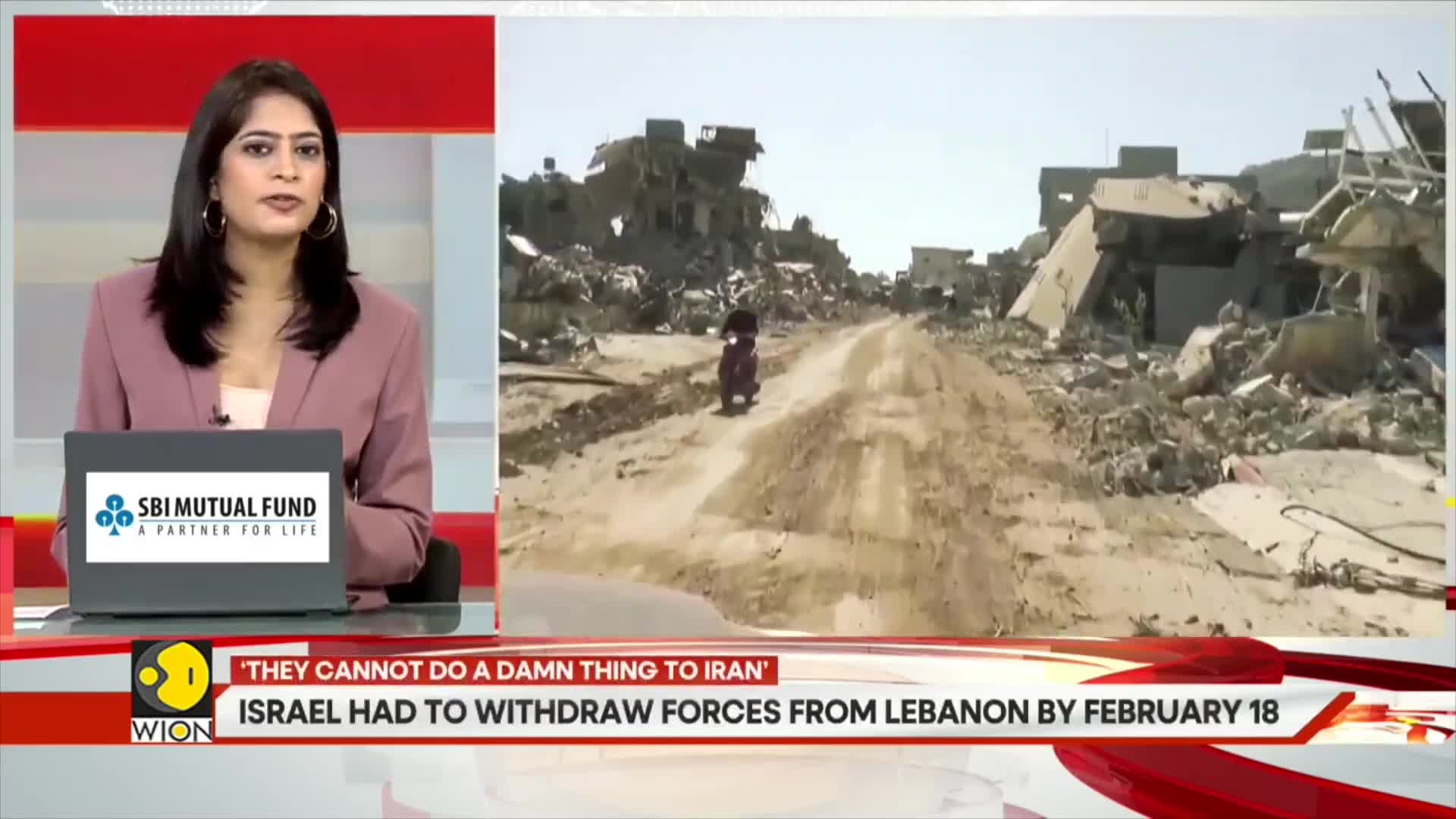
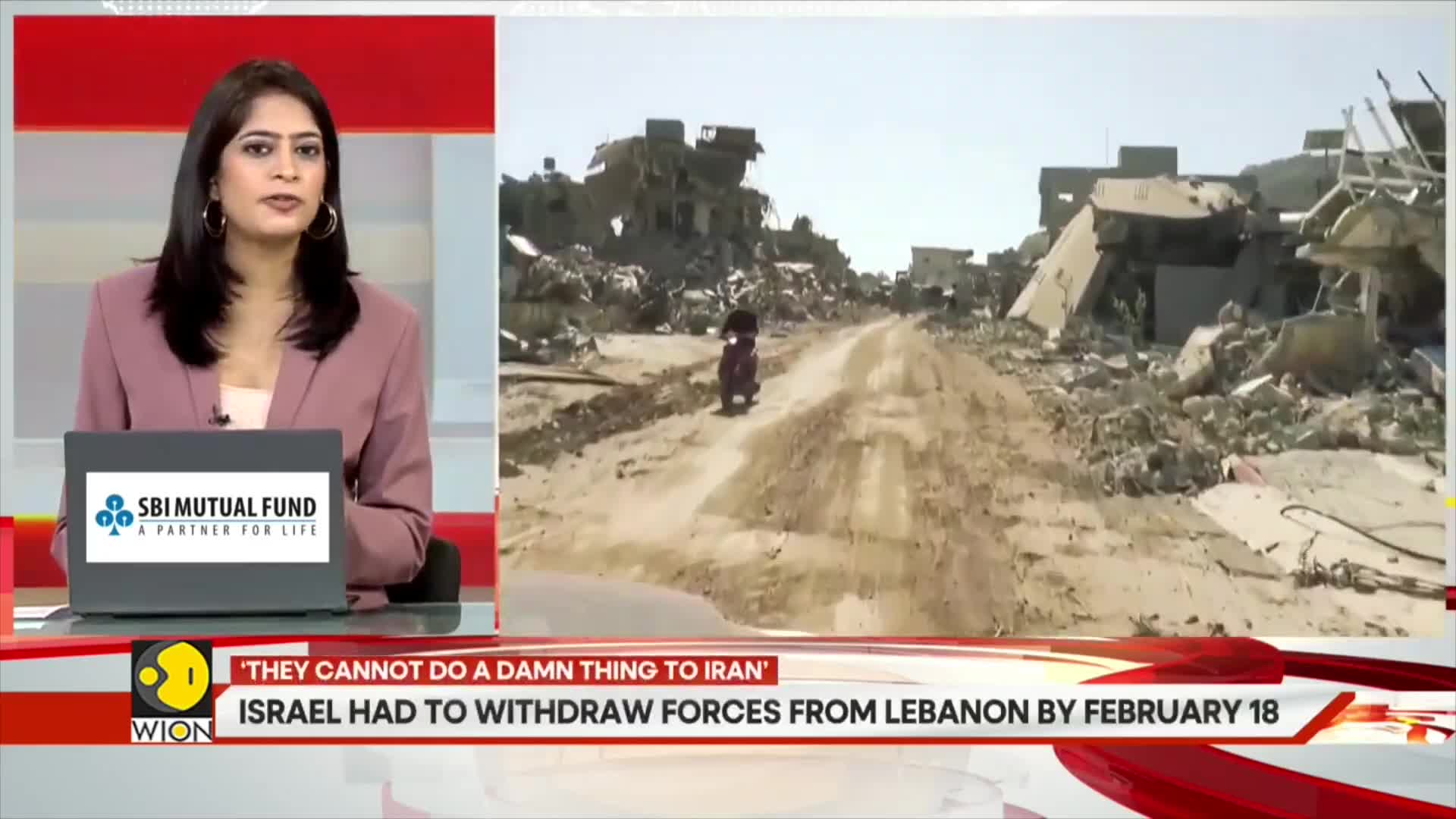
Watch clip answer (02:35m)What is the current record temperature in Rio de Janeiro?
Rio de Janeiro is experiencing extreme heat with temperatures reaching 44 degrees Celsius in the western part of the city. This marks the highest temperature recorded in Rio since 2014, according to the municipality's alert system. This unprecedented heatwave has triggered significant concerns as the city faces potentially dangerous conditions during what appears to be one of its most severe heat events in nearly a decade.
Watch clip answer (00:08m)How are residents in the Bateau Muje favela coping with the extreme heat in Rio de Janeiro?
In the Bateau Muje favela located in western Rio de Janeiro, residents are employing simple but effective cooling strategies to combat the severe heatwave. Their primary method involves dousing themselves with water to reduce their body temperature amid unbearable conditions where temperatures have reached up to 44 degrees Celsius. This community is particularly vulnerable as favelas often function as urban heat islands, intensifying the already extreme temperatures. These cooling efforts have become essential for daily survival as the city faces a level four heat alert, all while preparations for the upcoming Carnival festivities continue despite the challenging climate conditions.
Watch clip answer (00:06m)How is Rio de Janeiro's extreme heat affecting local events and activities?
Rio's unprecedented heatwave is significantly disrupting normal activities across the city. Residents flocked to beaches to cool off during the sizzling weekend, while a leading Samba School was forced to cancel its parade rehearsal on Copacabana beach due to extreme temperatures reportedly exceeding 44 degrees Celsius. The heatwave is affecting both cultural events and sports, with tennis stars facing challenging conditions both on and off the court. This extreme weather highlights how climate change is impacting daily life and traditional celebrations in Brazil's cultural capital.
Watch clip answer (00:13m)What extreme weather events has Brazil been experiencing in recent years?
Brazil has been experiencing a series of extreme weather events in recent years, with the state of Sao Paulo and Southeast currently under alert due to the first heat wave of the year, recording temperatures around 38 degrees Celsius. These severe weather conditions extend beyond heat waves to include floods, droughts, and fires across the country. Experts have linked these increasingly frequent and intense extreme weather patterns to global warming, indicating a concerning climate trend for the region. The current heat alert highlights Brazil's vulnerability to climate change impacts and the growing challenges faced by urban populations, particularly in densely populated areas.
Watch clip answer (00:16m)