Fiber Optic Networks
Fiber optic networks represent a revolutionary advancement in communications technology, utilizing thin strands of glass or plastic fibers to transmit data as pulses of light. This innovative method enables significantly higher bandwidth and faster data transmission speeds compared to traditional copper networks, making fiber optics the backbone of modern telecommunications. The components of a fiber optic system include optical fibers, transceivers for converting electrical signals to light, and amplifiers that boost signals over distance, ensuring minimal signal loss and immunity to electromagnetic interference. As a result, these networks are essential for high-speed internet, cloud infrastructure, and cable television, providing robust connectivity solutions for both residential and commercial applications. The importance of fiber optic networks continues to grow as demands for faster, more reliable internet connectivity escalate globally. Recent advancements such as hollow-core fibers and multi-core technologies promise to enhance data transmission capabilities even further, enabling the integration of fiber optics with 5G, AI, and the Internet of Things (IoT). With projections indicating sustained market growth in fiber deployment, particularly in underserved regions, it's evident that fiber optic technology is not just a critical infrastructure component but also a key driver of economic development and digital transformation. As industries increasingly rely on fiber to support everything from telemedicine to autonomous vehicles, the shift to this high-capacity, durable network is shaping the future of connectivity.
What is the purpose and importance of undersea cable networks for internet connectivity?
Undersea cable networks are essential infrastructure for global Internet connectivity, enabling local telecom operators to provide internet services to customers and connect different countries. These cables facilitate cross-border communication while helping telecom companies expand their network infrastructure and alleviate data congestion. Meta's investment in such cables comes at a critical time of increasing demand from telecom operators seeking to enhance their service capabilities and address growing bandwidth requirements.
Watch clip answer (00:22m)What is Project Water Worth and what regions will it connect?
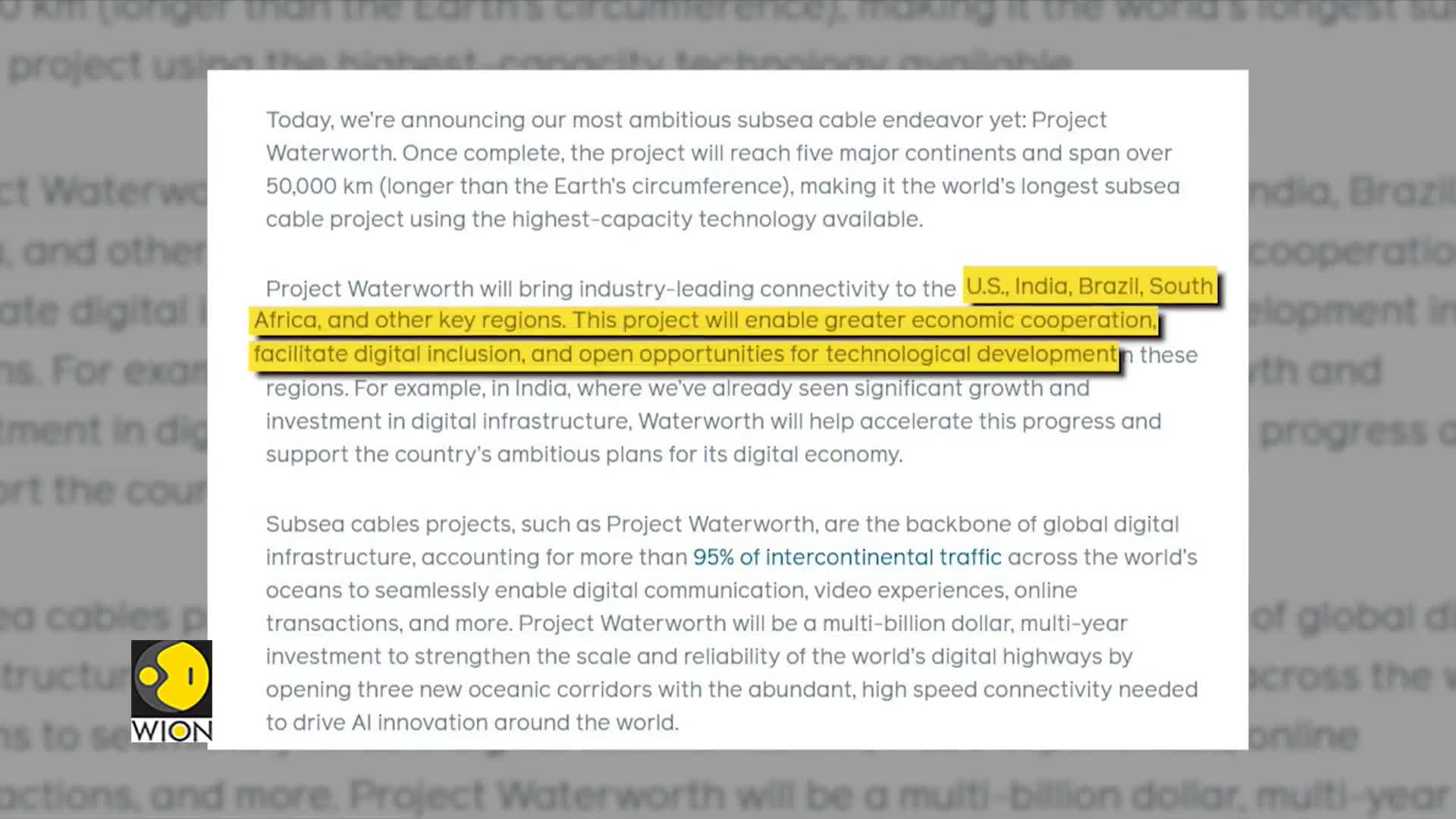
Project Water Worth is Meta's ambitious initiative to build the world's longest undersea cable, spanning 50,000 kilometers and connecting five continents. This multi-billion dollar, multi-year investment will link the United States, India, Brazil, South Africa, and other key regions through a subsea cable network. Once completed, Meta claims the cable system will be longer than Earth's circumference, making it the world's longest underwater cable project. The initiative represents a significant advancement in global connectivity infrastructure that will enhance digital communication across major continental regions.
Watch clip answer (00:32m)How is Meta protecting its Project Water Worth subsea cable network from potential damage?
Meta is implementing sophisticated protection measures for Project Water Worth by deploying advanced routing and innovative cable burial strategies. These techniques are specifically designed to safeguard the infrastructure in high-risk areas such as shallow coastal waters, where undersea cables are particularly vulnerable to damage. These protective measures are crucial as undersea cable networks form the backbone of global Internet connectivity, enabling local telecom operators to provide reliable Internet services to their customers and connect different countries. The protection strategies will help ensure the longevity and reliability of this ambitious 50,000 km cable project spanning five continents.
Watch clip answer (00:23m)