Environmental Sustainability
Environmental sustainability is the responsible management and utilization of natural resources aimed at meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This concept is integral as it ensures a stable and healthy environment through responsible practices that protect ecosystems, reduce carbon footprints, and promote the use of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. The urgency of environmental sustainability is underscored by the increasing challenges of climate change, water scarcity, and biodiversity loss, which demand coordinated efforts from individuals, businesses, and governments alike. Recent discussions highlight the role of sustainable practices across various sectors, including agriculture and the arts, where innovative solutions are being developed to address environmental concerns. For instance, sustainable agriculture techniques, such as crop rotation and water-smart farming, not only enhance food security but also minimize ecological disruption. In the corporate world, businesses are increasingly adopting environmental, social, and governance (ESG) frameworks to reduce their ecological impact while promoting transparency and accountability. As the United Nations emphasizes in its Sustainable Development Goals, fostering environmental sustainability is crucial for ensuring the health of our planet while supporting long-term human welfare and economic growth. By integrating sustainability into daily practices, societies can work towards a resilient future that balances economic advancement with the preservation of our natural environment.
What are the key differences between cloud seeding and chemtrails, and how does cloud seeding actually work?
Cloud seeding is a legitimate weather modification technology that uses scientific methodologies to enhance precipitation by introducing particles into clouds to increase rainfall efficiency. Unlike conspiracy theories about chemtrails, cloud seeding is conducted with statistical validation and real-time data monitoring, showing measurable increases in precipitation over targeted areas compared to control regions. The process involves hiring specialized companies to seed clouds in drought-stricken areas, helping fill reservoirs, support agriculture, and maintain stream levels for environmental protection. The visible streaks often seen in the sky are typically contrails from aircraft condensation, not cloud seeding operations, which use precise scientific techniques rather than widespread atmospheric spraying.
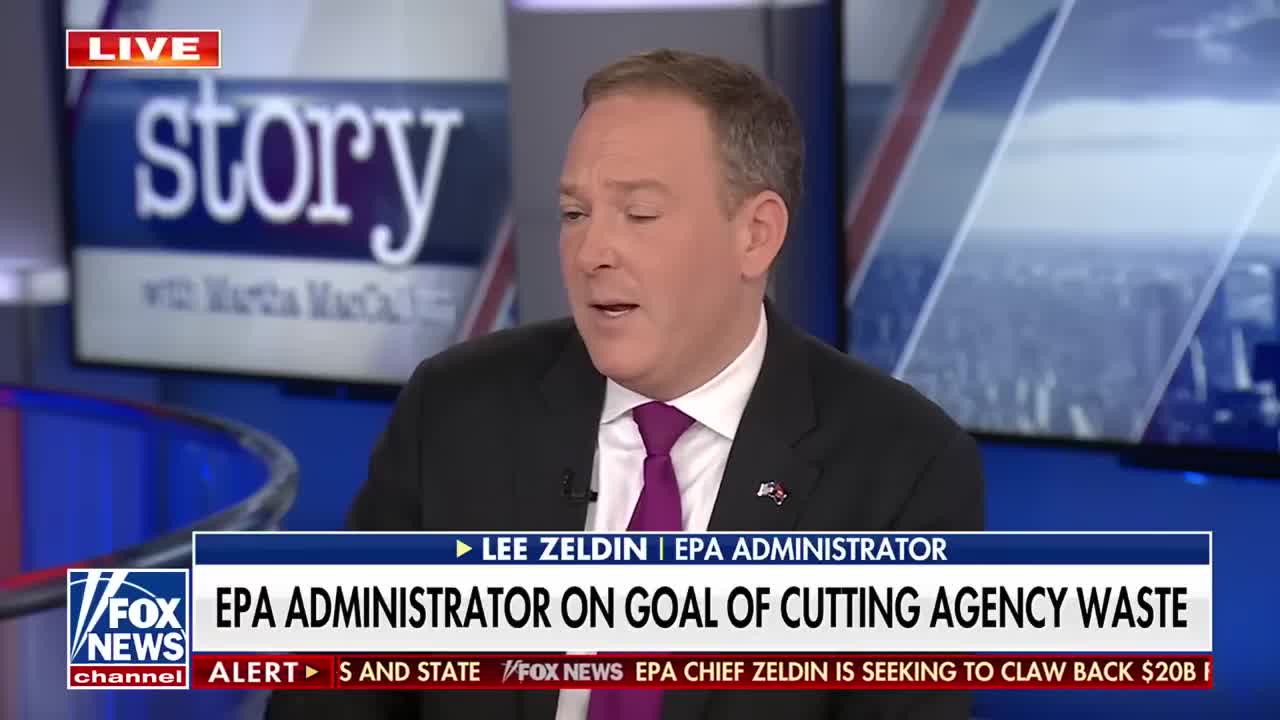
Watch clip answer (01:59m)What are the major oversight and accountability concerns that EPA Administrator Lee Zeldin has identified regarding the distribution of taxpayer funds at the Environmental Protection Agency?
EPA Administrator Lee Zeldin has raised serious concerns about the hasty distribution of $20 billion in taxpayer funds to eight private entities with minimal oversight. The administrator revealed that some entities were specifically created just to receive this funding, raising questions about accountability and proper vetting processes. Additionally, Zeldin has taken corrective action by canceling controversial grants, including a $50 million allocation to a climate advocacy group, and highlighted risks from mismanaged funds, particularly citing issues with a Canadian electric bus manufacturer's bankruptcy that could impact taxpayer investments.
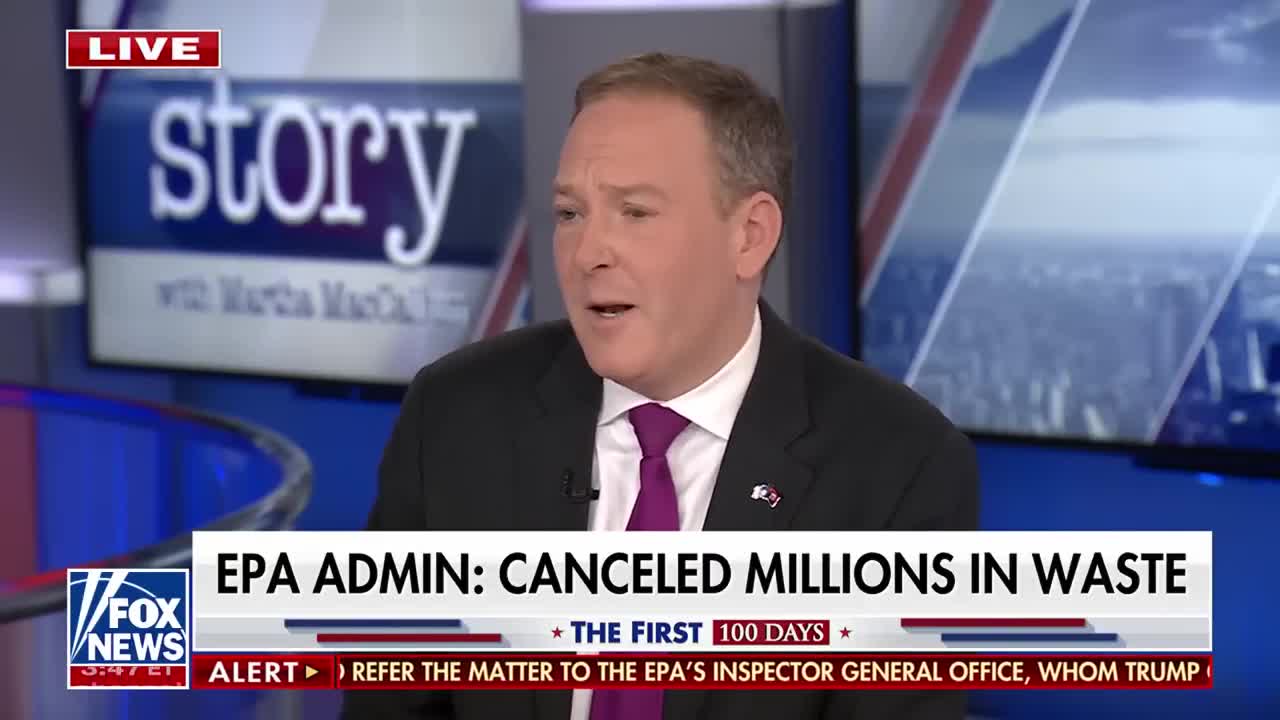
Watch clip answer (00:17m)What are the key environmental initiatives and responses being implemented by the EPA under the Trump administration's leadership?
The EPA under Lee Zeldin's leadership is focusing on ensuring Americans have access to clean air, land, and water as part of the "Great American Comeback Initiative." The agency is currently conducting the largest wildfire response in EPA history in Los Angeles, with over 1,200 workers surveying thousands of sites. President Trump has set an ambitious 30-day deadline to complete phase one hazardous material work, demonstrating the administration's commitment to rapid environmental response and restoration efforts.
Watch clip answer (00:39m)How does the concept of carbon footprint shift environmental responsibility from corporations to individuals?
The carbon footprint concept strategically redirects environmental accountability from major corporations to individual consumers. This narrative encourages people to focus on their personal, often minimal contributions to environmental problems rather than addressing the massive industrial impact of large companies. By promoting individual responsibility through carbon footprint awareness, corporations effectively deflect attention from their significant environmental damage. This allows mega-corporations to continue environmentally harmful practices while making individuals feel both guilty about their impact and satisfied with small personal changes. The strategy creates a false sense of environmental progress by emphasizing personal actions while the largest contributors to environmental degradation continue operating with minimal accountability or systemic change.
Watch clip answer (00:05m)How do large corporations like DuPont Chemical contribute to environmental destruction under capitalist democratic systems?
DuPont Chemical serves as a prime example of how major corporations exploit regulatory gaps in capitalist democracies to cause severe environmental damage. Under the current system in the United States, the company has been able to dump toxic waste into agricultural lands, contaminating natural water supplies and destroying fragile ecosystems with minimal consequences. This ongoing environmental destruction highlights a fundamental flaw in how capitalist democracies handle corporate accountability. Despite operating within a democratic framework that theoretically provides oversight, companies like DuPont continue these harmful practices, demonstrating the need for stronger regulatory mechanisms and systemic reforms to protect environmental integrity and public health.
Watch clip answer (00:13m)