Energy Infrastructure
Energy infrastructure is a complex network that includes the systems and physical assets required for the generation, transmission, storage, and distribution of energy resources such as electricity, natural gas, and oil. This essential framework supports vital economic activities and quality of life, playing a crucial role in connecting renewable energy systems like solar and wind to consumers. Power grid infrastructure is fundamental in managing the growing demand for energy, particularly with the increasing electrification trends and the substantial rise in consumption from data centers and electric vehicles. Amidst these advancements, energy storage solutions, including battery technologies, have become critical for maintaining reliability and balancing supply and demand fluctuations. The urgency of enhancing energy infrastructure is underscored by the rapid transition towards decarbonization and the challenges imposed by climate change and geopolitical tensions. Ongoing investments focus on modernizing grids with smart technologies to improve efficiency and resilience against threats like natural disasters and cyberattacks. As renewable energy sources dominate new capacity additions, accounting for over 90% of recent U.S. generation, the integration of these systems into an aging infrastructure demands immediate attention and coordinated global efforts. Recent reports emphasize that despite substantial investments, significant gaps remain, necessitating continuous innovations and policies that promote sustainable energy practices and ensure the security of energy supplies. With these developments, the future of energy infrastructure will hinge on balancing the needs for reliability, affordability, and environmental sustainability.
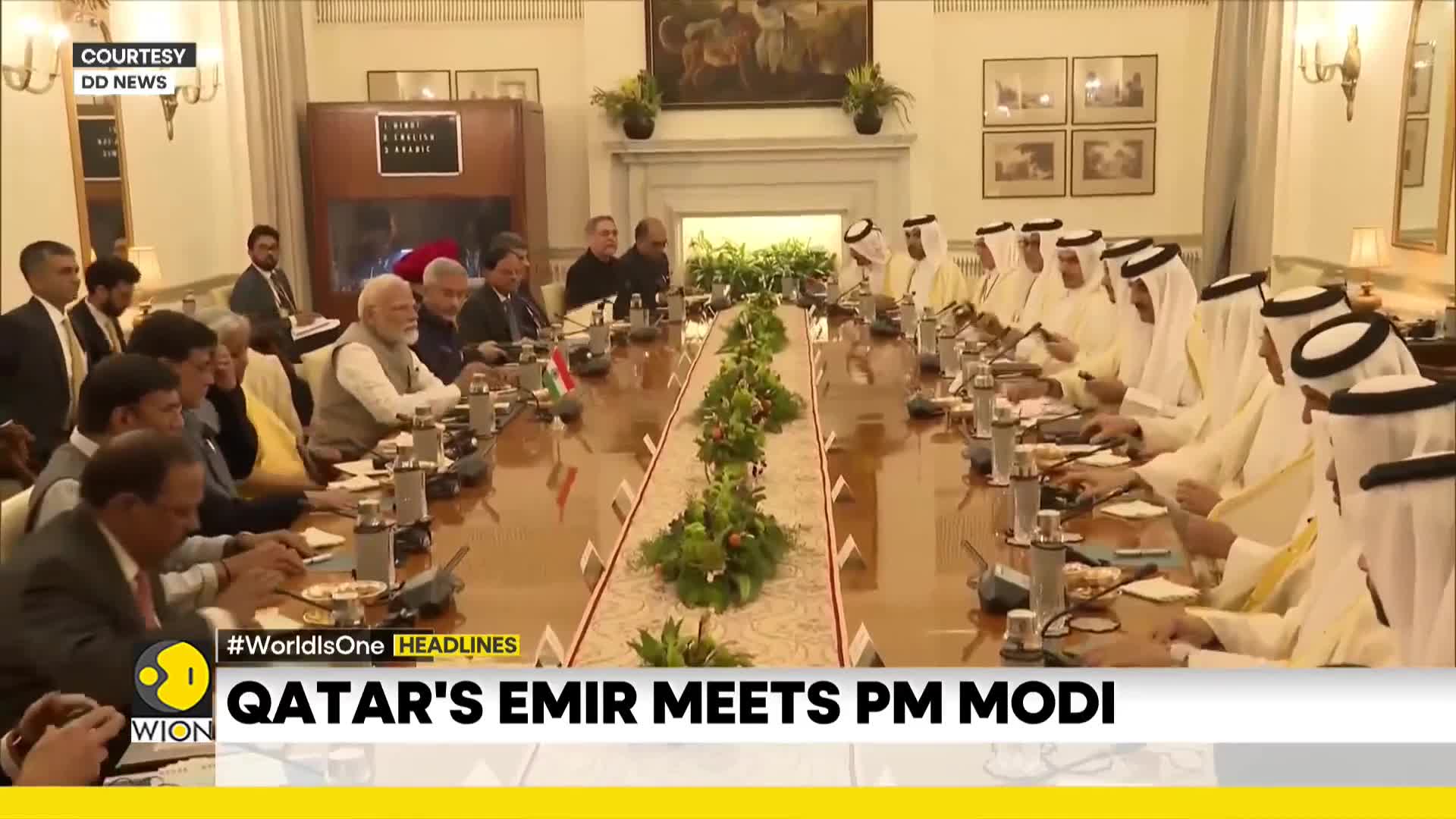
What key agreements were signed during Qatar's Emir Sheikh Tamim Bin Hamad Al Thani's visit to India?
During the Emir's two-day official visit to India, multiple significant agreements were signed between the two nations. These included an agreement on establishing a strategic partnership between India and Qatar, as well as an agreement for the avoidance of double taxation and prevention of fiscal evasion with respect to taxes on income. The visit also resulted in discussions about potentially signing a free trade agreement in the future. Both countries are targeting to double their bilateral trade to $28 billion in the next five years while also exploring ways to broaden energy cooperation.
Watch clip answer (01:35m)What are the two key elements that form the basis of the India-Qatar relationship?
The India-Qatar relationship is fundamentally built on two key elements. First, Qatar serves as an important source of LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) to India, making it a crucial energy partner in India's strategy. This energy cooperation forms the backbone of their economic ties. Second, the large Indian diaspora residing in Qatar represents a significant human connection between the two nations. During recent bilateral meetings, Prime Minister Modi and the Amir of Qatar signed important agreements including a strategic partnership and a revised double taxation treaty, aiming to strengthen these foundational elements of their relationship.
Watch clip answer (00:37m)What weather challenges are affecting the Central U.S. and Kentucky?
A brutal winter storm is sweeping across the Central U.S., with cold alerts extending from Canada to Central Texas. Sub-zero wind chills are affecting Montana and the Dakotas, while parts of the Central Plains are bracing for up to a foot of snow. In Kentucky, the situation is particularly concerning as thousands of residents remain without power or safe drinking water following deadly weekend flooding. The state now faces the dual challenge of recovering from flood damage while preparing for the incoming winter storm, creating urgent conditions for emergency response efforts.
Watch clip answer (00:27m)What is Japan's plan to transform its energy mix to meet climate targets?
Japan plans to significantly transform its energy mix, which is currently the dirtiest among G7 nations. Nearly 70% of Japan's power needs in 2023 were met by coal, gas, and oil-burning plants, which Tokyo aims to reduce by 30-40% in the coming years. Nuclear power will play a major role in helping Japan meet growing energy demands from AI and microchip factories while reducing emissions. These changes support Japan's ambitious goals of cutting greenhouse gas emissions by 60% by 2035 and transitioning to renewable energy as the primary power source by 2040.
Watch clip answer (00:31m)What challenges is Germany's energy transition currently facing?
Germany's ambitious energy transition is stalling due to political turmoil that has frozen key climate funding. The most significant impact is on a 2 billion euro hydrogen project that has been put on hold amid the crisis. This situation signals a broader and concerning shift away from green priorities in Germany's policy agenda. As funding remains frozen, the country's ability to maintain momentum toward its climate goals is increasingly in question, creating uncertainty for both national energy security and international climate commitments.
Watch clip answer (00:15m)What is OPEC's current plan regarding oil supply despite market speculation?
OPEC is firmly maintaining its plan to increase oil supply starting in April 2023, despite growing speculation about possible delays to this scheduled increase. Russian Deputy Prime Minister Alexander Novak has explicitly dismissed reports suggesting any reconsideration of this plan. Industry insiders remain optimistic about market conditions, suggesting that global oil markets have the capacity to absorb this additional supply without significant disruption. This steadfast approach indicates OPEC's confidence in current market dynamics and its strategic direction for global oil supply management.
Watch clip answer (00:16m)