Crimea Annexation
The annexation of Crimea by Russia is a pivotal event in modern history, marking a significant escalation in the Russia-Ukraine conflict that has had enduring global repercussions. Occurring in March 2014 amidst Ukraine's political turmoil following the ousting of President Viktor Yanukovych, this controversial takeover involved unmarked Russian soldiers, referred to as "little green men," who swiftly seized control of key infrastructure in the Crimean Peninsula. Following a disputed referendum on March 16, in which local authorities claimed over 95% approval for joining Russia, President Vladimir Putin formally annexed Crimea two days later, asserting that this act was necessary to protect ethnic Russians in the region. However, this action was widely condemned internationally as illegal under international law, violating Ukraine's territorial integrity and leading to significant sanctions against Russia. The strategic significance of Crimea cannot be overstated. As a critical naval asset located in the Black Sea, Crimea has long been a focal point of military and political tensions between Russia and the West. The annexation not only exacerbated existing hostilities but also established a precedent for the use of military force to alter borders, a concern that has since reverberated through international relations. The ongoing conflict has seen numerous escalations, with Crimea acting as a vital staging ground for further Russian military actions in Ukraine, including recent aggressions. Recently, legislative efforts in the U.S. and discussions in international forums have sought to reinforce the stance of non-recognition of the annexation, emphasizing the importance of maintaining Ukraine’s sovereignty and the need for a resolution to this unresolved geopolitical flashpoint.
What is Trump's evolving strategy regarding Ukraine's conflict?
Trump's administration is quickly moving to thaw relations with Russia in preparation for a potential deal over Ukraine. The strategy involves asking European allies to take on more responsibility while signaling to Ukraine that they likely won't regain control of Donbass and Crimea due to limited military prospects for reclaiming these territories. This represents a significant shift in U.S. policy toward a negotiated peace solution rather than supporting Ukraine's territorial integrity at all costs. The administration's swift action to secure Fogle's release is viewed as part of this broader diplomatic effort to reset relations with Russia ahead of potential peace negotiations.
Watch clip answer (00:22m)Why did Central and Eastern European nations join NATO after the Soviet collapse?
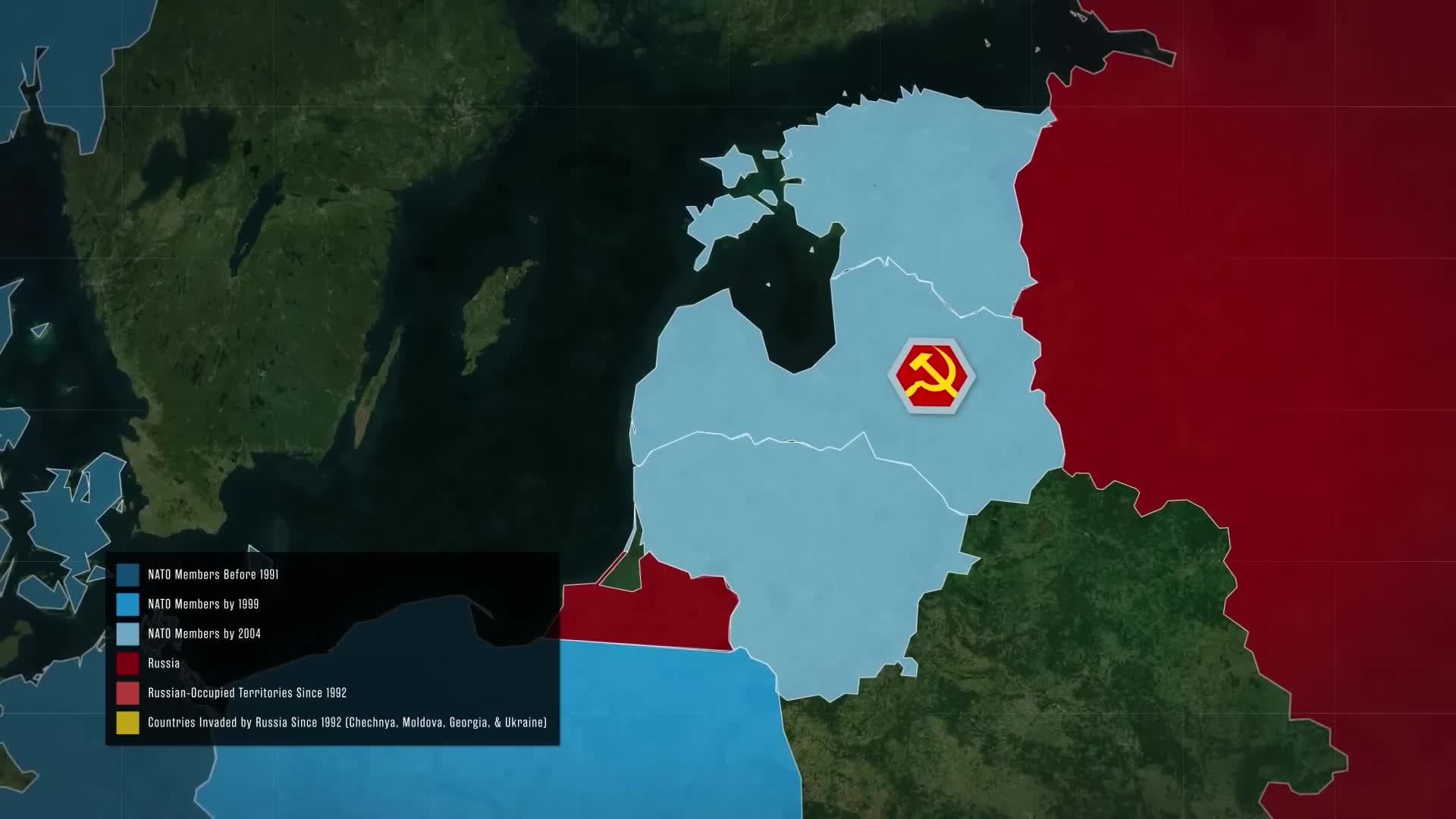
Following the Soviet collapse, Central and Eastern European states joined NATO primarily out of fear that Russia might use the approximately 800,000 ethnic Russians left in their countries as a pretext for future invasion and conquest. These nations didn't wait for NATO to move eastward - rather, they actively sought western protection against potential Russian aggression. NATO demonstrated restraint by not establishing permanent foreign military bases in these nations until after Russia's invasion of Ukraine and seizure of Crimea in 2014. The concerns of these nations were ultimately validated by Russia's subsequent military actions in Georgia in 2008, intervention in Syria, and the invasions of Ukraine since 2014 that have resulted in hundreds of thousands of casualties.
Watch clip answer (00:47m)What is the major concern facing NATO and European security?
The major concern is that US President Donald Trump may scale back or completely withdraw American troops from Europe, particularly from the Baltic states where over 5,000 soldiers are stationed. Currently, about 100,000 American troops are deployed across Europe, alongside approximately 100 B61 nuclear gravity bombs at six NATO bases in five European countries. This potential withdrawal has sent shockwaves across the continent as European officials view it as a significant security risk. The implications are severe: a potentially weakened NATO alliance, an emboldened Russia, and deepening divisions within the European Union over how to respond. These concerns arise during the ongoing Ukraine war when Europe stands at a security crossroads.
Watch clip answer (01:18m)What are the key goals of the U.S. in the peace negotiations with Russia regarding Ukraine?
According to the report, Secretary of State Marco Rubio outlined four key goals for diplomatic relations and conflict resolution between the U.S. and Russia regarding Ukraine. The main points of contention include Ukraine's NATO membership status, territories annexed by Russia, and establishing a framework for lasting peace. Despite President Zelenskyy's absence, the U.S. aims to engage Russia in meaningful dialogue to explore potential cooperation pathways. This meeting represents a significant step in reopening high-level discussions between the two nations after prolonged tensions over the Ukraine conflict.
Watch clip answer (00:01m)What does the message from Washington suggest about Ukraine's territorial ambitions?
After three years of intense fighting with thousands of casualties, the message from Washington appears to undermine Ukraine's hopes and raises doubts about its goal to reclaim all lost territories. This affects not only Crimea, which Russia annexed in 2014, but also the four regions of Luhansk, Zaporizhzhia, Kherson, and Donetsk that Russia annexed in 2022. The American stance signals a potential shift in support for Ukraine's territorial ambitions, suggesting that full reclamation of all occupied areas might not align with current U.S. diplomatic positioning in talks with Russia. This development represents a significant challenge to Ukraine's stated objectives in the ongoing conflict.
Watch clip answer (00:28m)What are Russia's demands regarding Ukraine in the ongoing conflict?
Russia demands that Ukraine withdraw its troops from regions annexed in September 2022, including Crimea, Donetsk, Luhansk, Zaporizhzhia, and Kherson. Beyond currently occupied territories, Russia insists Ukraine cede additional territory in eastern and southern Ukraine (approximately 30% of areas Russia doesn't yet control), disband its military, and become a demilitarized neutral state. Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov has firmly dismissed any possibility of Russia making territorial concessions in negotiations. Additionally, Russia may extend demands to include reduction or full withdrawal of NATO forces from Eastern European countries including Poland, the Baltic States, and Romania as part of broader demilitarization requirements.
Watch clip answer (01:08m)