Aerospace Engineering
Aerospace engineering is a vital discipline within the field of engineering that focuses on the design, development, testing, and operation of vehicles that navigate both the Earth’s atmosphere and outer space. This dynamic field consists of two primary branches: aeronautical engineering, which pertains to aircraft operating within the atmosphere, and astronautical engineering, which deals with spacecraft and rockets operating beyond it. Aerospace engineers utilize principles from physics, mathematics, and engineering to innovate and solve complex design challenges, aiming to enhance aircraft efficiency, safety, and performance. The significance of aerospace engineering has seen a marked increase in recent times, driven by the urgent need for sustainable and technologically advanced solutions within the industry. Key trends such as the development of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF), hybrid-electric propulsion systems, and urban air mobility technologies underscore the field's relevance. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and digital transformation further streamlines processes, from aircraft design software to manufacturing and supply chain management. As global demand for aerospace engineering jobs and career opportunities continues to grow, prospects appear promising, with entry-level positions and job placements in high demand. By addressing the latest advancements, challenges, and innovations, aerospace engineering plays a crucial role in shaping the future of aviation and space exploration, making it an increasingly pivotal area of study and professional pursuit.
Why must pilots maintain control during the entire landing process, especially in windy conditions?
Pilots must maintain complete control throughout landing because the process isn't complete upon touchdown. As Scott Pattillo explains, relaxing control prematurely can be catastrophic, especially with gusting winds that can catch a wing. These wind gusts can force a wing to hit the ground, potentially causing the aircraft to cartwheel and flip over. Even after touching down, pilots must actively fly the airplane until reaching the end of the runway. Maintaining situational awareness and active control prevents dangerous scenarios where wind can destabilize the aircraft during its most vulnerable phase of flight, ensuring passenger safety during challenging landing conditions.
Watch clip answer (00:15m)What are the key specifications and features of the Tejas Aircraft?
The Tejas is a compact light combat aircraft with a 13.2-meter length and 8.2-meter delta wing configuration, making it one of the world's smallest supersonic multirole fighters. It features a service ceiling of 16,000 meters, range of 3,000 kilometers, and payload capacity of 5,300 kg. The aircraft is equipped with indigenous technology, including the U Tam active electronically scanned array radar that can track 50 targets at 100km range. Its weaponry includes R73 short-range missiles, Astra Mk 1A beyond visual range missiles, and potentially the Brahmos NG cruise missile. The Tejas offers high maneuverability due to its delta wing design while balancing cost-effectiveness with advanced avionics.
Watch clip answer (09:11m)What is NASA's X59 aircraft and how will it impact commercial air travel?
NASA's X59 is a revolutionary X plane designed to usher in the next era of supersonic flight technology. This groundbreaking aircraft is engineered to dramatically reduce travel times, specifically cutting flight duration from New York to Los Angeles in half. The X59 represents a significant advancement in aerospace engineering that could fundamentally transform commercial aviation by making supersonic travel more accessible and efficient for passengers worldwide.
Watch clip answer (00:12m)How extensive is NASA's current space exploration program and what is the relationship between science and exploration?
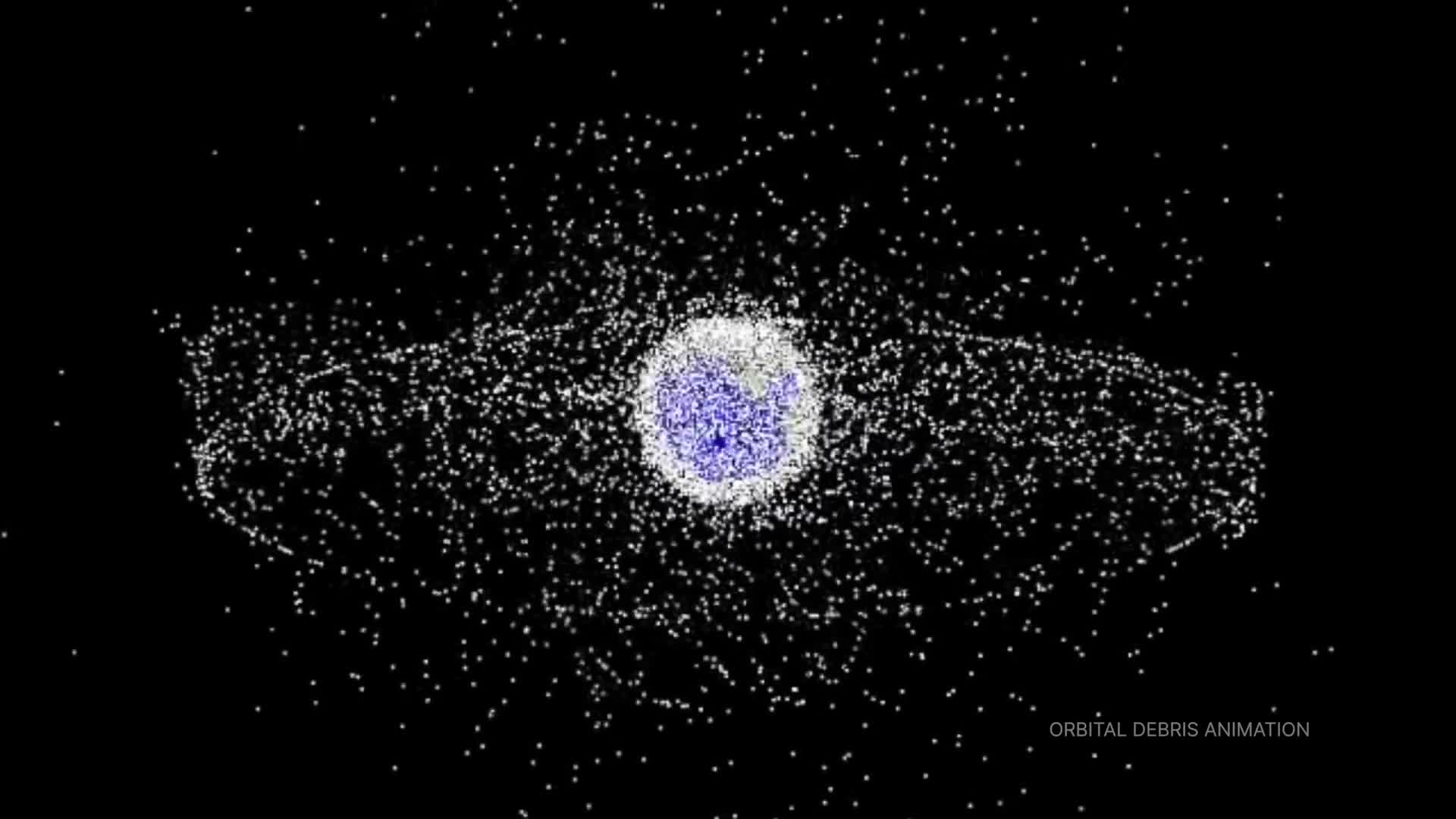
NASA currently operates 140 active missions across the solar system, demonstrating the unprecedented scope of human space exploration. The relationship between science and exploration is symbiotic - scientific knowledge enables more ambitious exploration missions, while exploration activities generate new scientific discoveries and data. This interconnected approach allows NASA to continuously push the boundaries of human knowledge while advancing our capabilities to explore deeper into space, ultimately benefiting humanity through technological innovations and scientific breakthroughs.
Watch clip answer (00:13m)What are NASA's current major achievements and future plans for space exploration under the current administration?
NASA has achieved the monumental launch of the James Webb Space Telescope, marking a generational advancement in space observation capabilities. The agency is actively developing next-generation telescopes like the Nancy Grace Roman to explore potentially habitable worlds. Additionally, NASA is making significant progress on the Artemis program, with Artemis I successfully completing its mission and the Artemis 2 crew preparing for upcoming lunar adventures. The agency has also commissioned new lunar landers, advanced spacesuits, and rovers to support the return of American astronauts to the Moon's surface. These initiatives represent NASA's comprehensive strategy to advance human space exploration, from lunar missions to eventual Mars exploration, positioning the next generation of astronauts for unprecedented discoveries beyond Earth.
Watch clip answer (00:57m)What was the significance and outcome of NASA's Artemis II mission?
NASA's Artemis II represents a monumental achievement as the first crewed lunar mission in over 50 years. The 10-day journey successfully tested the Orion spacecraft's deep-space capabilities and emergency systems through an extraordinary orbit around the Moon. The mission concluded with the crew's safe return to Earth, marking their first time on solid ground after ten days in space. This historic mission demonstrates humanity's renewed ability to travel to deep space and establishes the foundation for sustained lunar exploration and future missions to the Moon's far side.
Watch clip answer (00:08m)