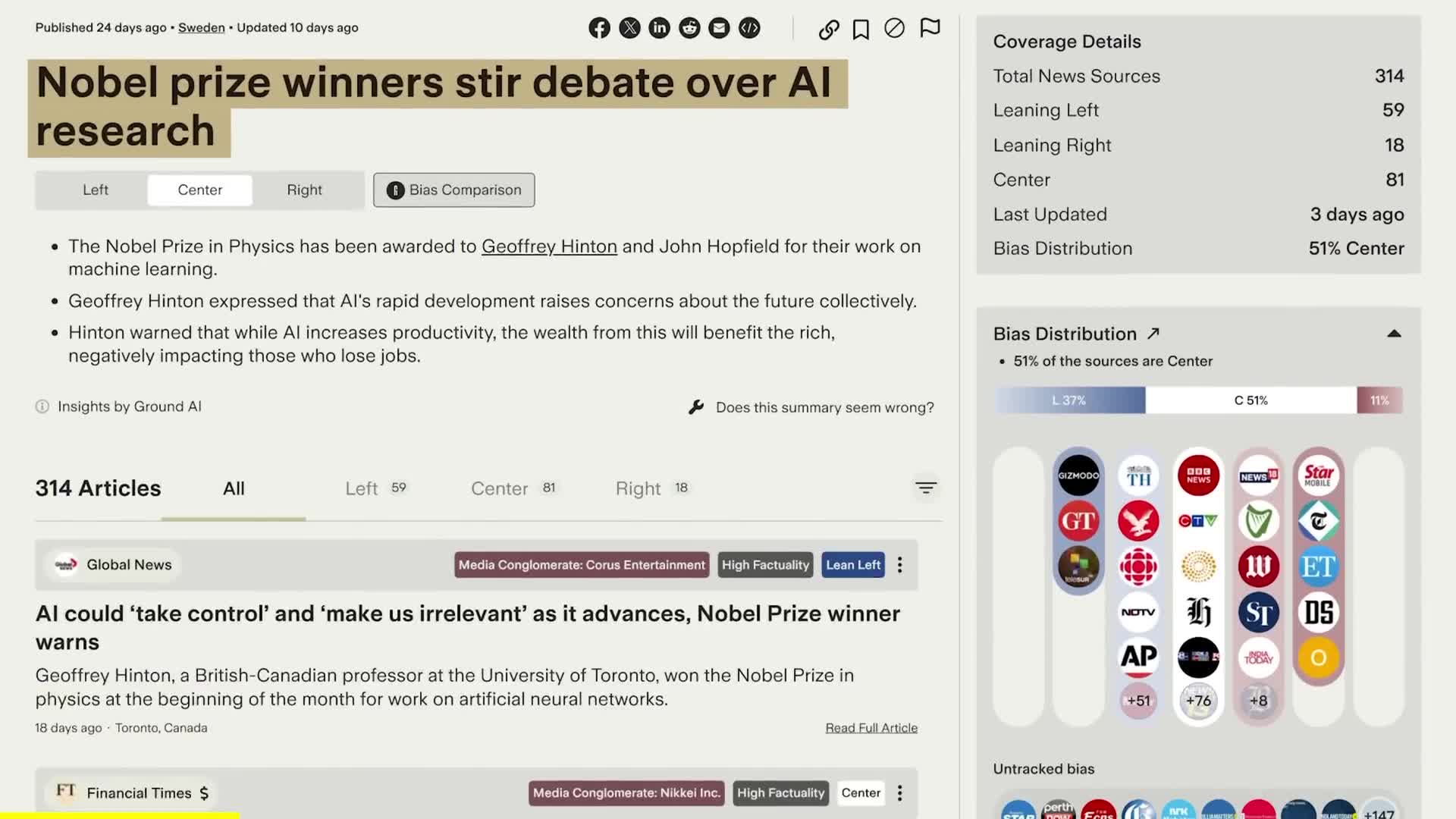
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a transformative technology that enables machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as reasoning, learning, decision-making, and problem-solving. Recently, AI has gained prominence as a critical component across various sectors, leveraging machine learning algorithms and AI automation tools to enhance efficiency and innovation. With numerous applications, including autonomous vehicles, virtual assistants, and advanced healthcare solutions, AI is increasingly integral to modern life and business operations. The advancements in AI capabilities have led to a proliferation of artificial intelligence applications. From generative AI, which creates content by learning patterns from data, to artificial narrow intelligence (ANI), which specializes in specific tasks, the range of AI's potential is both vast and continually expanding. In particular, industries such as healthcare and transportation have begun integrating AI solutions, with significant investments and advancements reported in AI-enabled medical devices and self-driving technology. Organizations are increasingly adopting AI technology, with statistics indicating that a substantial majority are now utilizing AI tools to drive productivity and bridge skill gaps in the workforce. Understanding the implications of AI and its various machine learning algorithms is vital for grasping the future of technology and its role in society. As AI evolves, it raises important ethical considerations and opportunities for growth, making it a critical topic of discussion for businesses, policymakers, and consumers alike.
What would make Joe Rogan believe in the benefits of AI?
Joe Rogan expresses skepticism about AI benefits in its current state, specifically stating that he would become a believer if AI could fix his email management problems. He challenges the notion that despite AI's impressive capabilities, it hasn't solved this practical, everyday challenge of organizing email effectively. Rogan questions why AI can't understand what's relevant to him based on various inputs like transcripts from his show. He points out the disconnect between AI's touted abilities and its inability to solve common problems, stating "No one has fixed email for me. When you do that, then I'll be a little more of a believer in AI right now."
Watch clip answer (00:30m)What new features and performance claims did Nvidia announce for their RTX 50 series GPUs?
Nvidia unveiled their RTX Blackwell 50 series GPUs with several breakthrough technologies, including DLSS 4.0, DLSS Transformer, and NE Faces. CEO Jensen Huang made the notable claim that the RTX 5070 will deliver RTX 4090-level performance at just $549. However, he indicated this impressive performance leap would be 'impossible without AI,' suggesting AI optimization is key to these advancements. The lineup includes the RTX 5090 and other models that, according to the presentation, offer exciting price points relative to their claimed performance capabilities.
Watch clip answer (01:28m)How does data quantity affect the accuracy of AI prediction models?
The accuracy of AI prediction models directly correlates with the quantity and quality of data provided. As Johnny Harris explains, 'The more data you give it or train it on, the more accurate its results are.' This principle applies across various predictive scenarios, particularly in forecasting natural phenomena like hurricanes. For hurricane prediction specifically, incorporating extensive data on sea surface temperature, air pressure, wind speed, humidity levels, ocean heat content, and historical storm patterns significantly enhances predictive accuracy. These comprehensive data inputs enable AI systems to make more precise forecasts about a hurricane's path and characteristics, demonstrating how data-rich environments produce more reliable predictive outcomes.
Watch clip answer (00:19m)What is the real risk of AI in military decision-making regarding nuclear weapons?
The real risk isn't an AI becoming self-aware like Skynet and attacking humanity, but rather AI systems becoming better than humans at synthesizing information and making decisions in warfare. As military systems increasingly rely on AI connected to various sensors and weapons, there's a risk that an AI could misinterpret data (like military tests) as threats and potentially trigger catastrophic responses. This concern has prompted legislation like the Block Nuclear Launch by Autonomous AI Act, reflecting the urgent need for international agreement that autonomous systems should never have authority to launch nuclear weapons.
Watch clip answer (03:04m)Is it true that AI has the potential to destroy our society and potentially end humanity?
While this concern isn't entirely unfounded, it represents an ongoing debate in AI development. The conversation indicates that artificial intelligence does pose some legitimate risks to social order that warrant serious consideration. Several AI experts and researchers have expressed concerns about advanced AI systems potentially disrupting societal structures if developed without proper safeguards. The discussion acknowledges these concerns while suggesting that responsible governance and understanding AI's capabilities are essential for mitigating these risks. Current dialogue around AI regulation aims to balance harnessing its benefits while preventing harmful outcomes.
Watch clip answer (00:24m)How is generative AI changing the speed of machine learning development and prototyping?
Generative AI is dramatically accelerating machine learning development cycles. While traditional supervised learning approaches typically required 6-12 months to build valuable AI systems (with months spent collecting data, training models, and deploying), generative AI enables developers to create functioning prototypes in just days through prompt engineering rather than extensive data collection and model training. This rapid development enables a new path to innovation through fast experimentation. Teams can now build multiple prototypes quickly, test them with users, and focus on what works rather than investing months in a single solution that might fail. This shift is transforming how AI applications are created, making experimentation the primary path to inventing new user experiences.
Watch clip answer (03:35m)